This blog will explain how you can execute a rapid activation of a set of FIORI lighthouse apps.
Questions that will be answered are:
- Which apps can be used for rapid setup?
- How to execute the rapid activation of FIORI lighthouse apps?
This blog assumes you have finished the basic activation of embedded FIORI on S4HANA, which is explained in this blog.
FIORI lighthouse apps
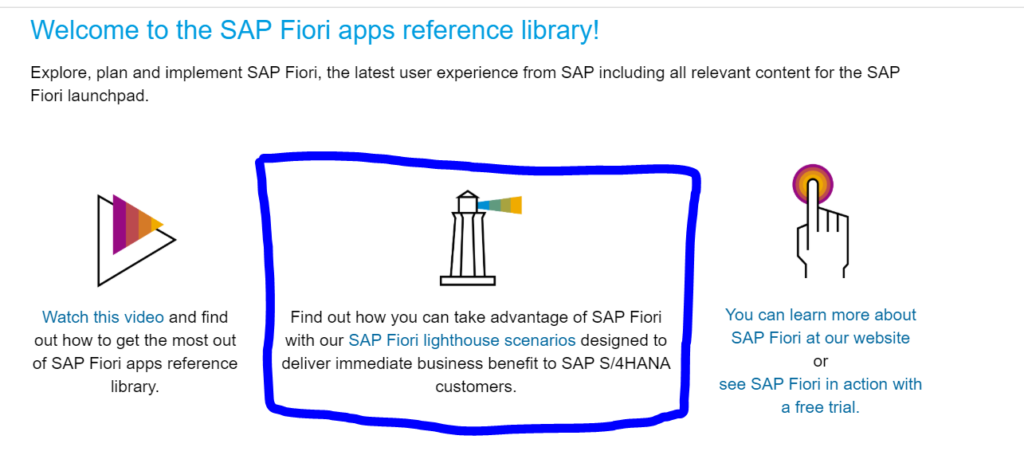
FIORI lighthouse apps are enabled for rapid activation. On the FIORI reference library site click on the Lighthouse scenario link to get a PDF full of all possible apps you can activate:
In the app finder you can also search for specific lighthouse apps:
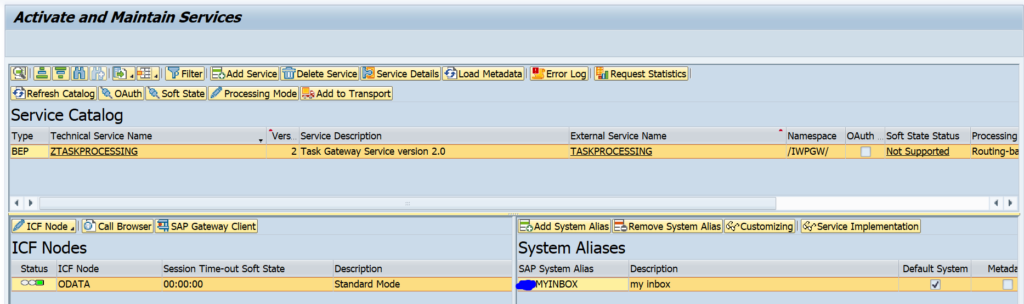
Rapid activation of FIORI lighthouse app
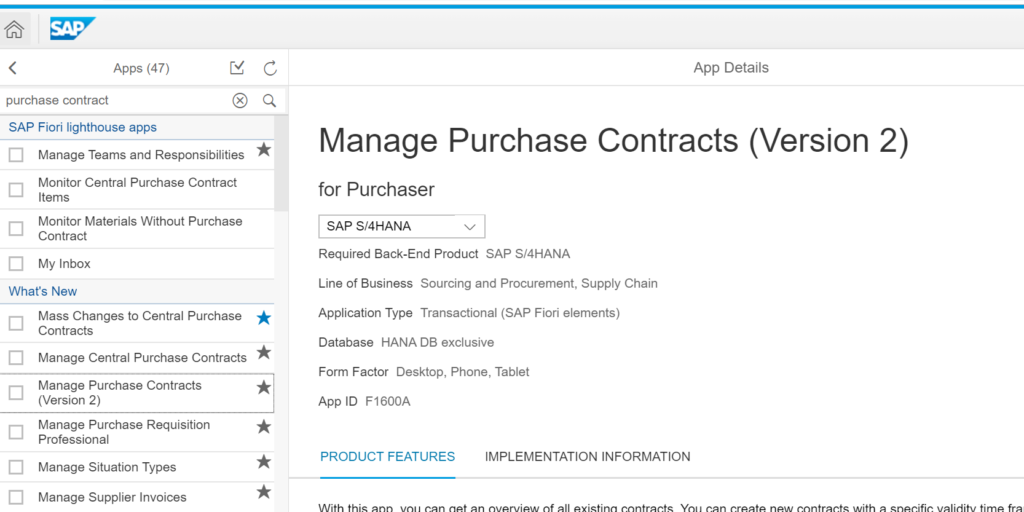
We will take the following app as example to execute the rapid activation: app ID F1600A: Manage Purchase Contracts (Version 2):
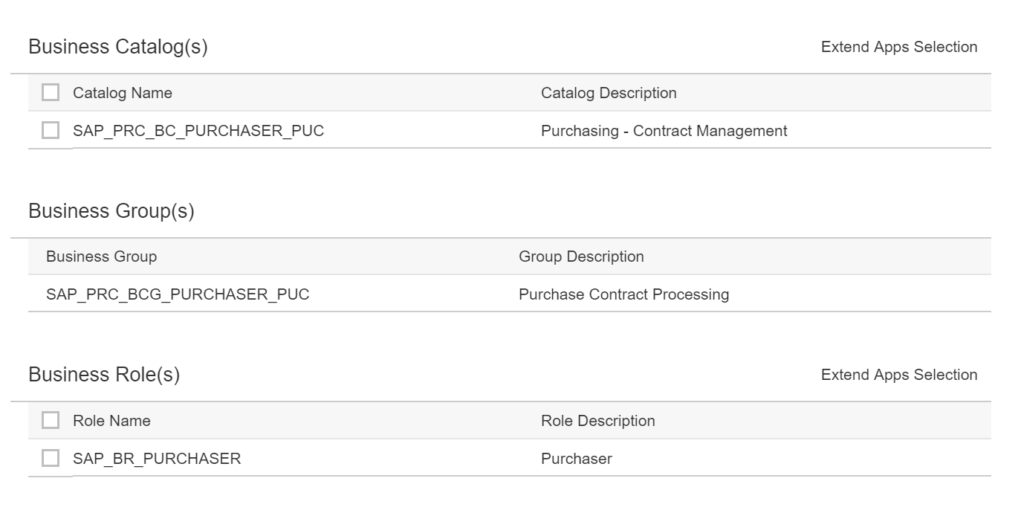
In the implementation information scroll down to the authorization information section:
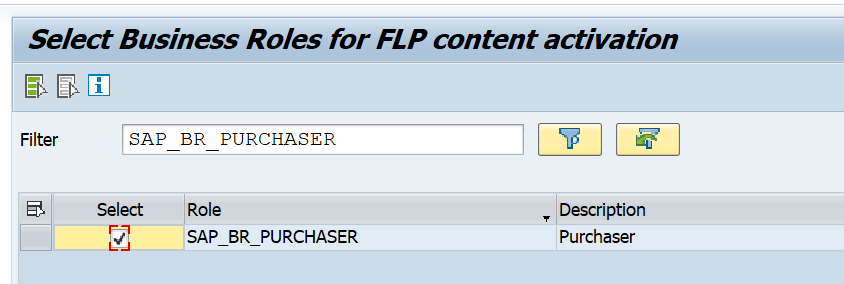
For now you can ignore the catalog and business group. Important here is the business role: SAP_BR_PURCHASER.
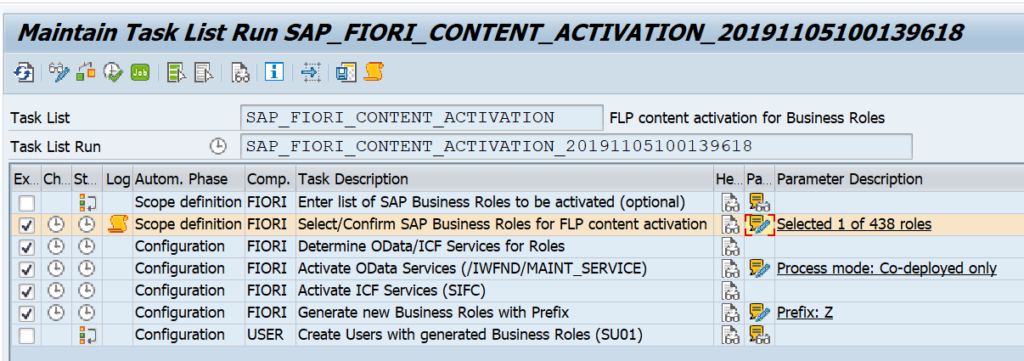
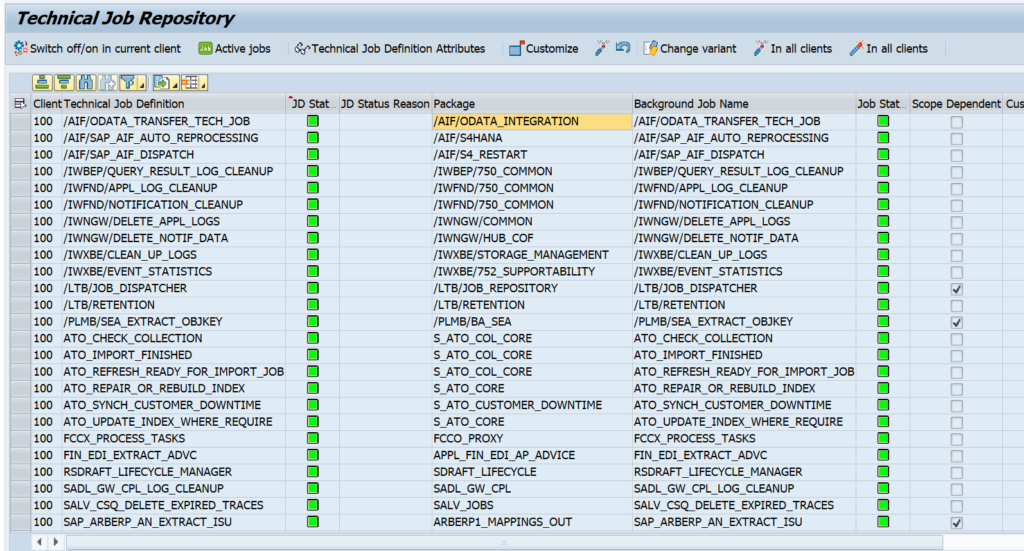
Go to transaction STC01 and select task list SAP_FIORI_CONTENT_ACTIVATION:
In the scope definition select the needed role SAP_BR_PURCHASER:
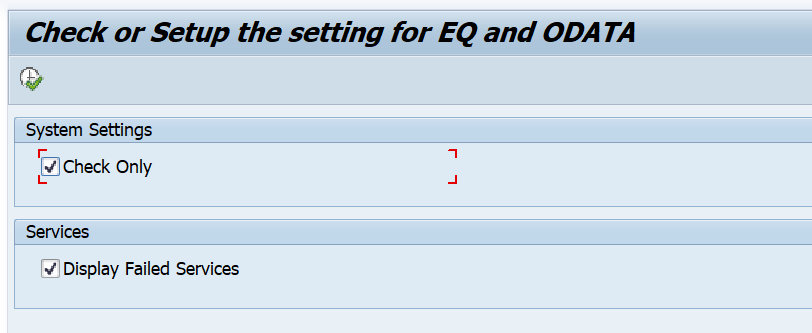
In the task list set the mandatory parameters process mode to co-deployment and Prefix to Z. Now start the task list execution and be patient. This might run up to 10 minutes.
This task list will now activate all ODATA services for the app group (not only for this single app, but the complete group!). It will activate all SICF nodes for the app group (yes, again the whole group). And it will generate the PFCG authorization role SAP_BR_PURCHASER.
If the task list is finished, assign the role SAP_BR_PURCHASER to your user ID.
Content activation for catalogs
For some scenarios it might be needed to activate catalog content. To do this, first apply OSS note 3339909 – Fiori Setup: Content Activation for Catalogs. This note delivers STC01 task list SAP_FIORI_FCM_CATALOG_ACTIVATION.
Testing
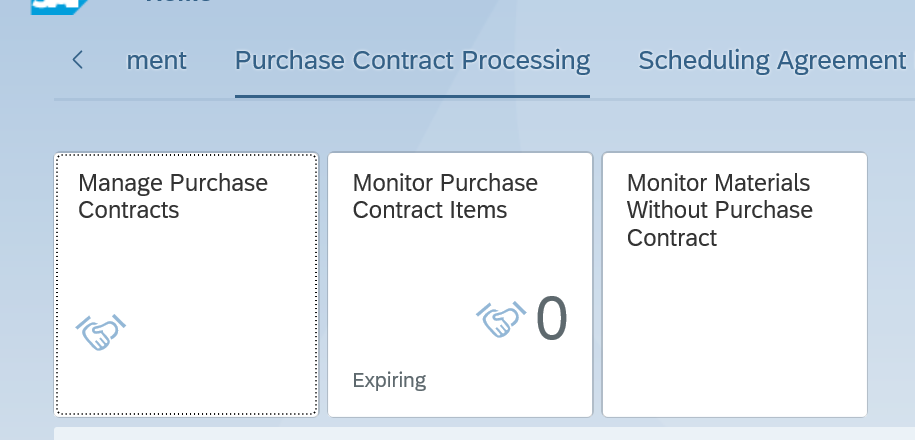
Start the FIORI launchpad (transaction code /UI2/FLP):
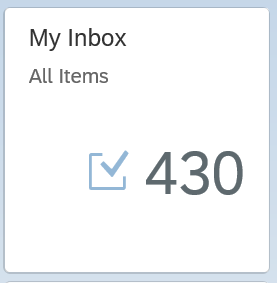
You see that the tile Manage Purchase Contracts is visible. Since we activated a complete group, also the other tiles are immediately visible.
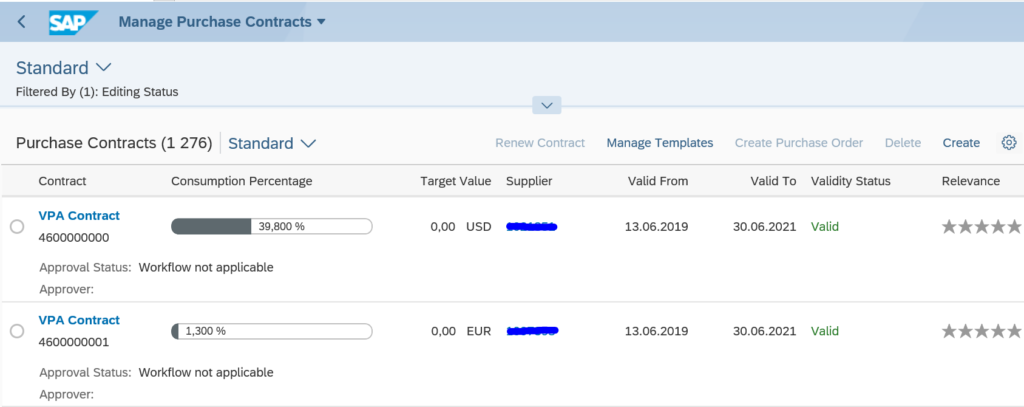
Clicking on the Manage Purchase Contracts tile gives immediate result:
This shows we can activate complete group of apps that immediately work, with minimal effort.
Issue detection
You can use the FIORI app support function to quicly analyze an issue in your newly activated FIORI app. Read more in this blog.
In app extensibility
All the FIORI lighthouse apps are built for in app extensibility. This allows you to change the look and feel of a standard SAP app and to add custom fields to standard SAP app. Read more in this blog.
Transport and activation after transport
After transport everything is present, but in inactive state. You need to perform the activation after transport.
OSS note 2886433 – Fiori Setup: Activation of OData Services in Prod Systems with task lists contains a perfect PDF that describes how to carry out the activation in a productive system using the proper selections in the task list.
Embedded activation and system refresh
If you refresh your sandbox, quality or development system with production copy, read this note 3111069 – Task list clarification post System copy/System Refresh in Embedded deployment on activation of embedded FIORI after the refresh.
OSS notes
Background OSS notes:
- 3085127 – Composite SAP note: Rapid Activation for SAP Fiori in SAP S/4HANA 2021
- 3236624 – Composite SAP note: Rapid Activation for SAP Fiori in SAP S/4HANA 2022
- 3336782 – Composite SAP note: Rapid Activation for SAP Fiori in SAP S/4HANA 2023
Bug fix notes to apply: