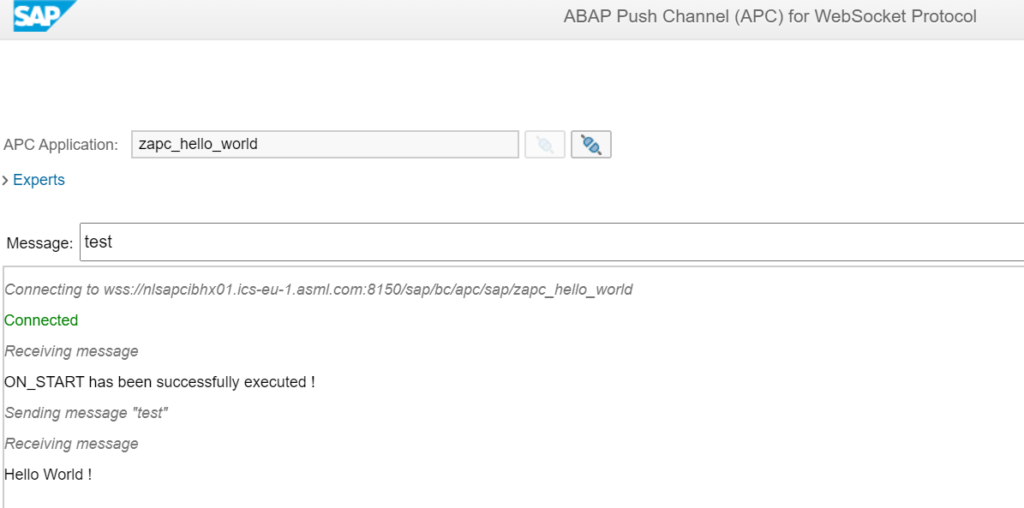
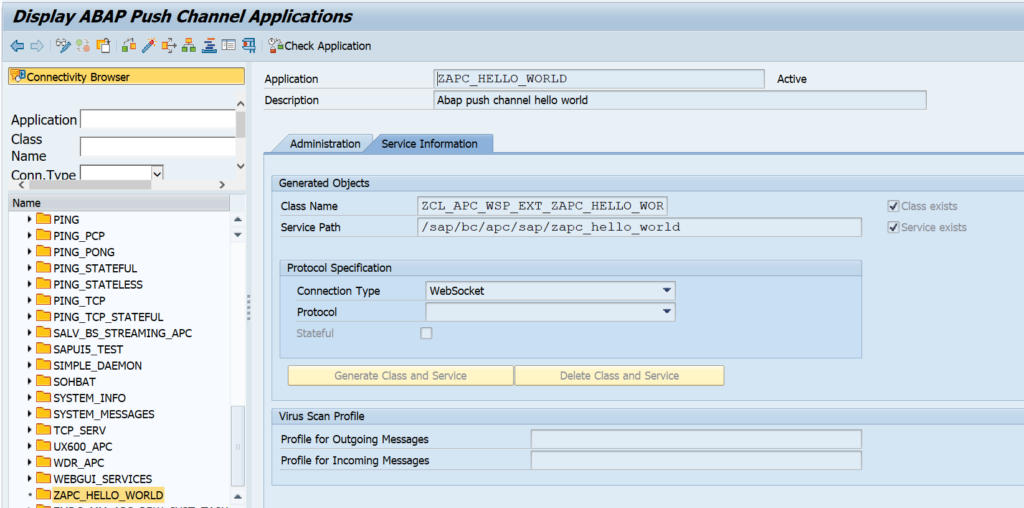
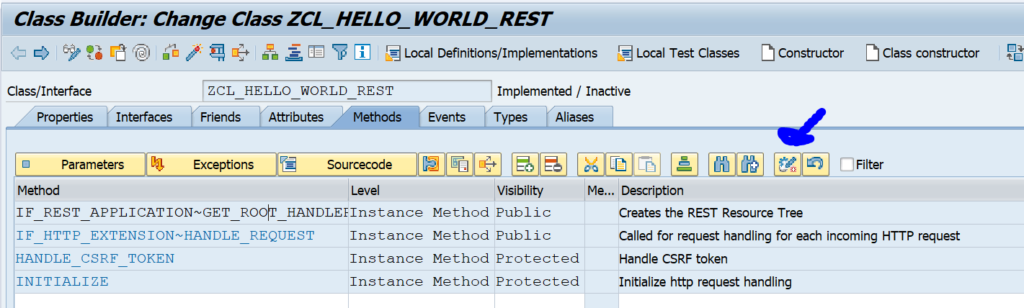
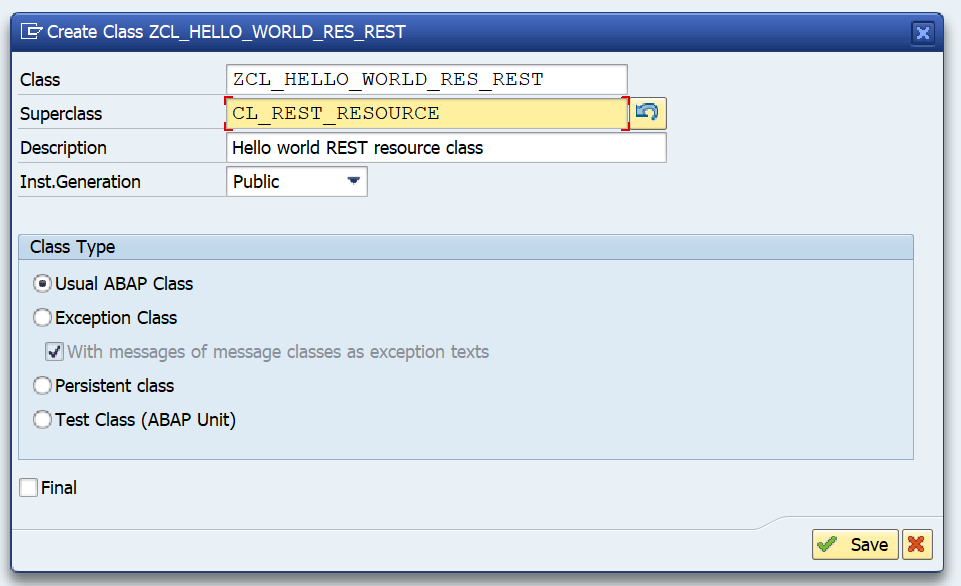
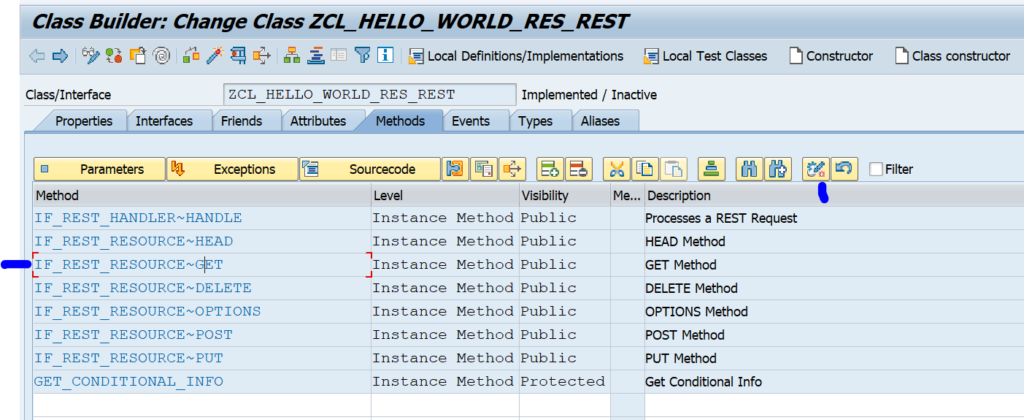
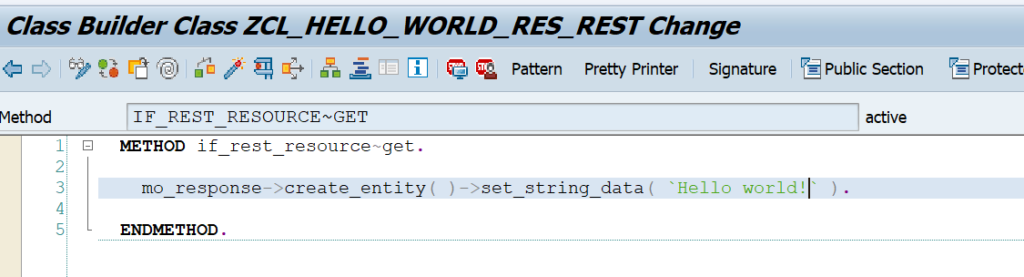
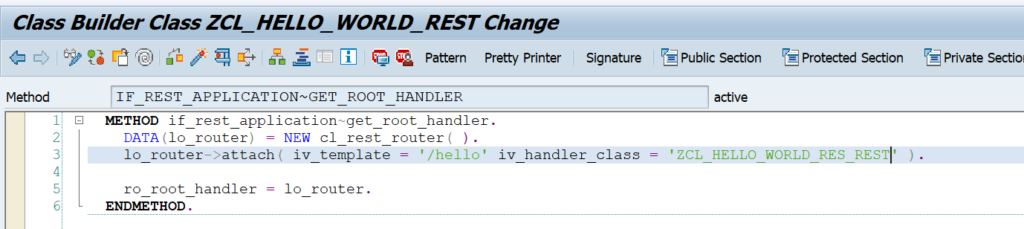
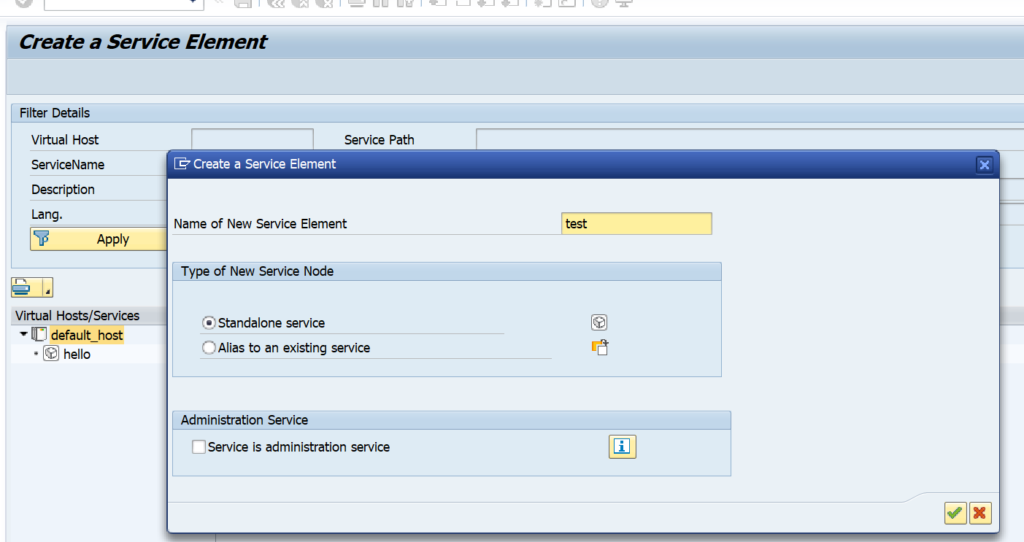
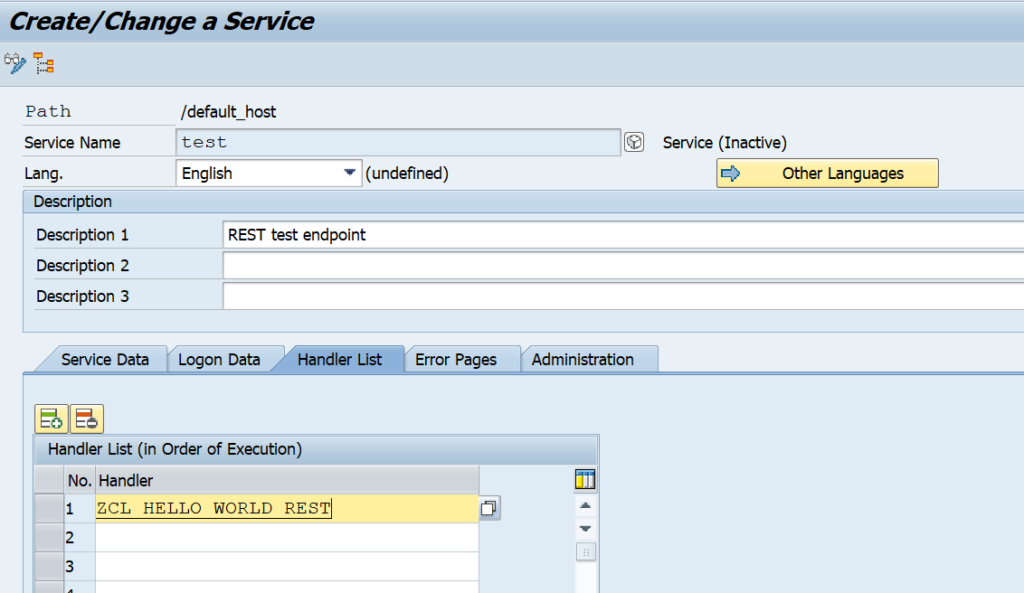
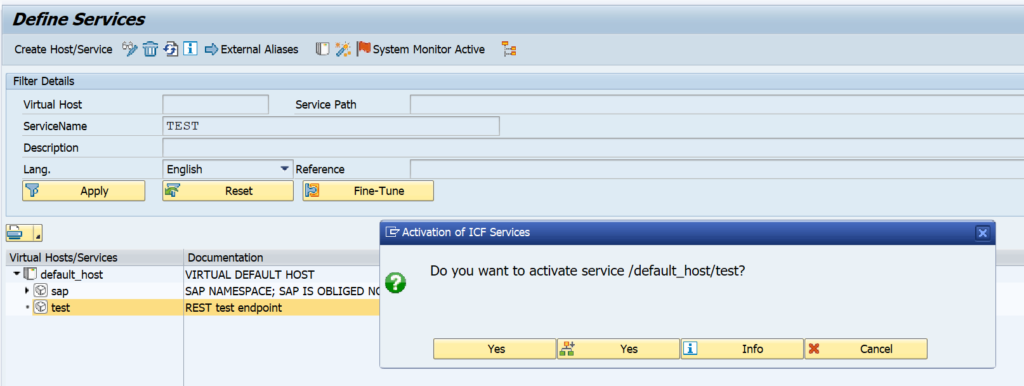
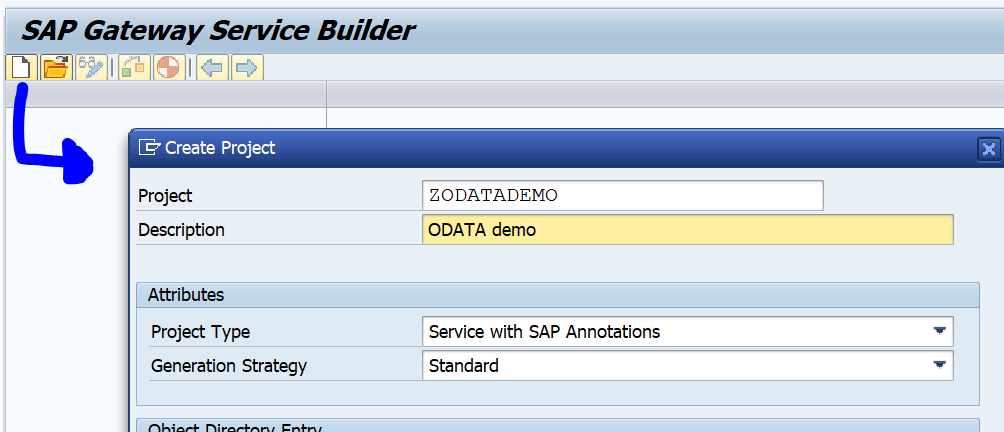
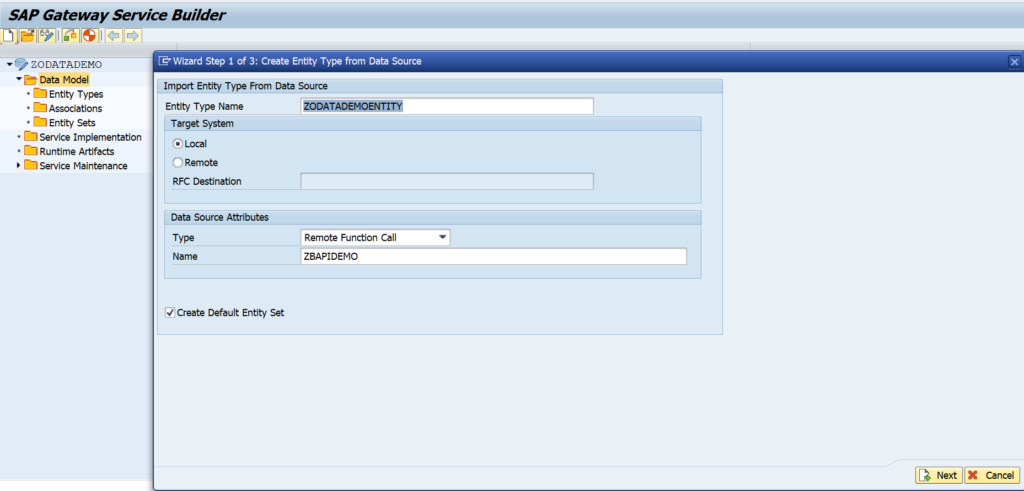
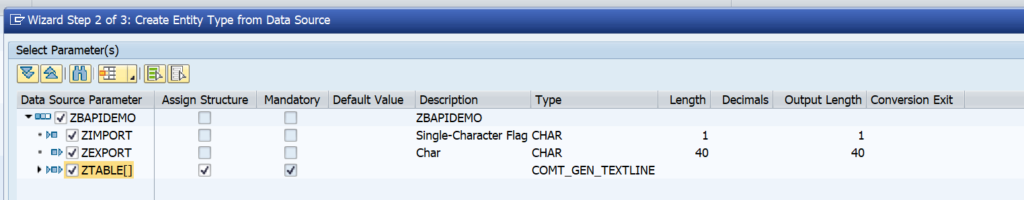
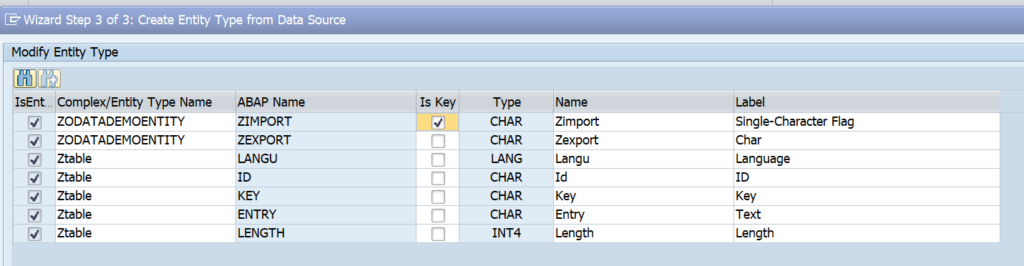
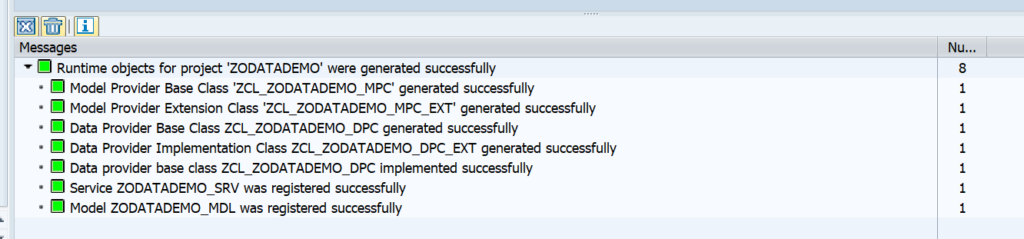
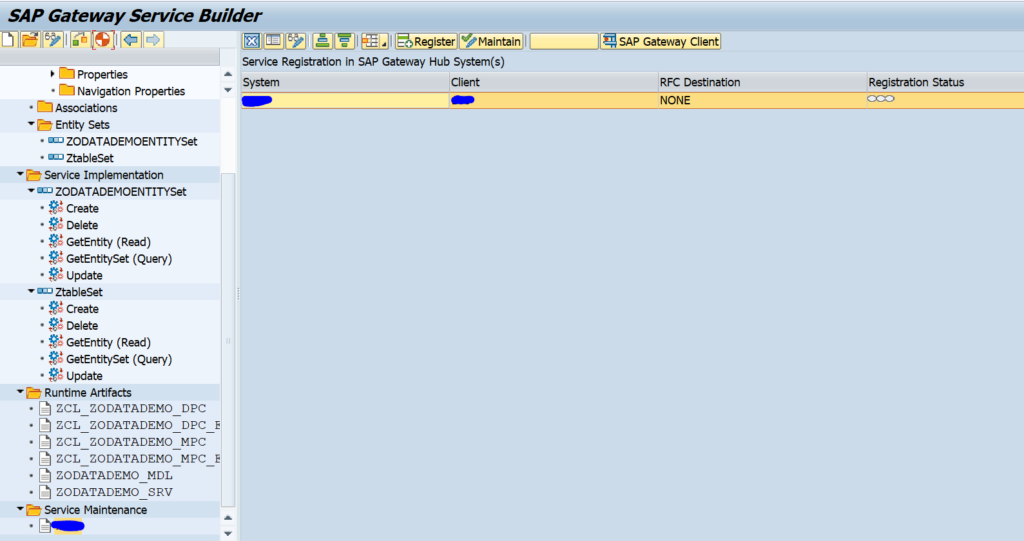
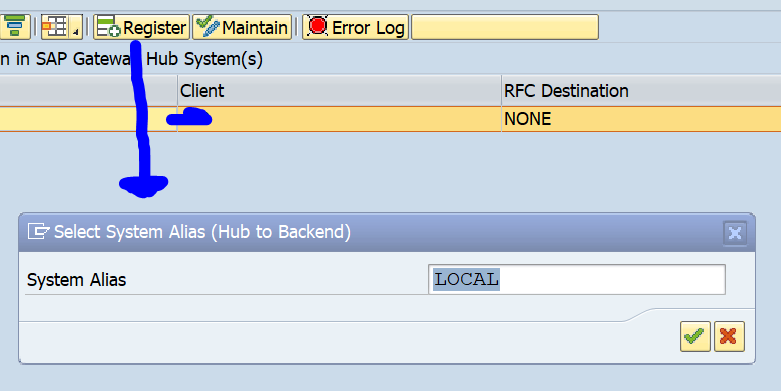
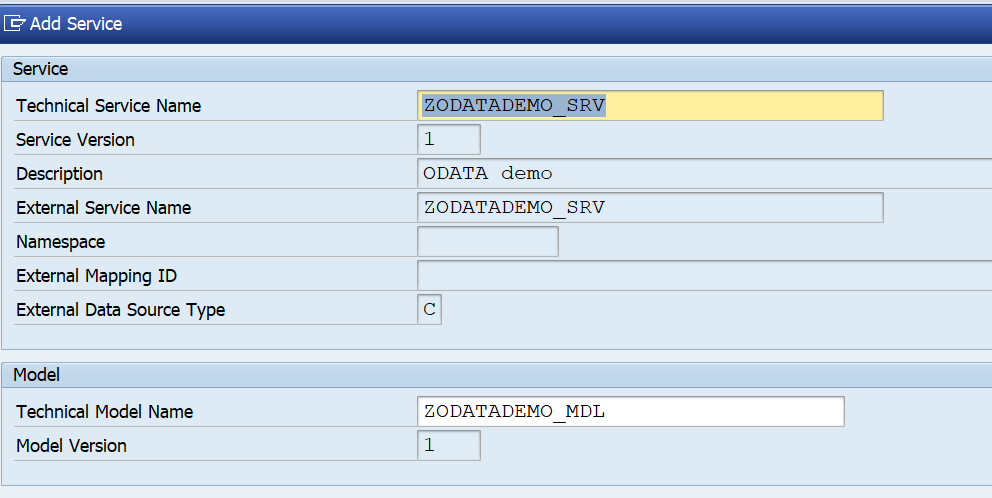
OAUTH can be called from custom ABAP. The explanation is given in this formal SAP help file. But it is quite complex.
In the example program below we will use OAUTH to call SAP BTP CPI.
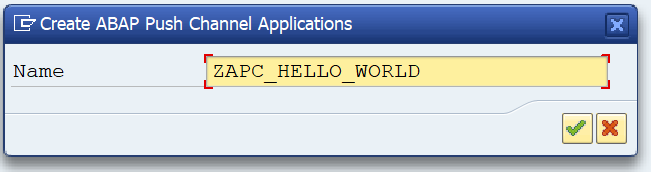
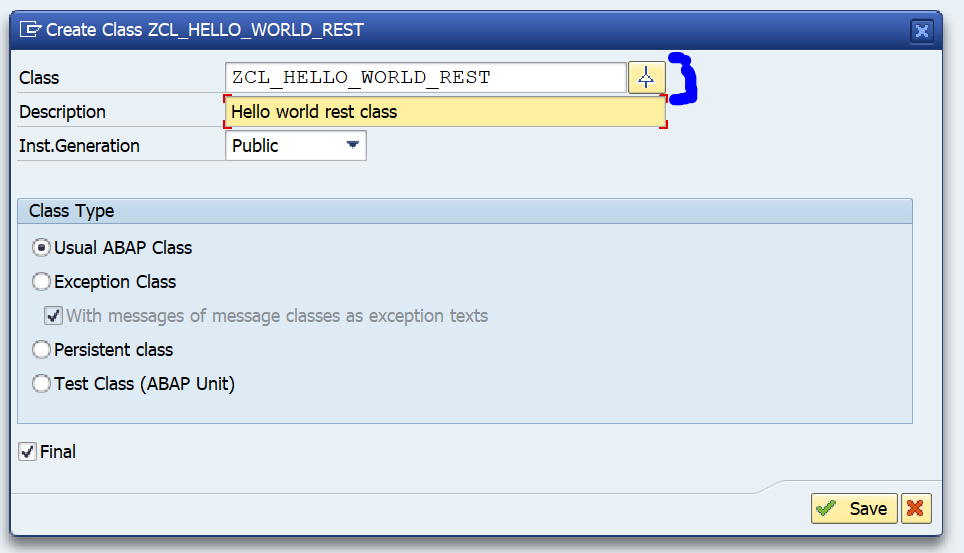
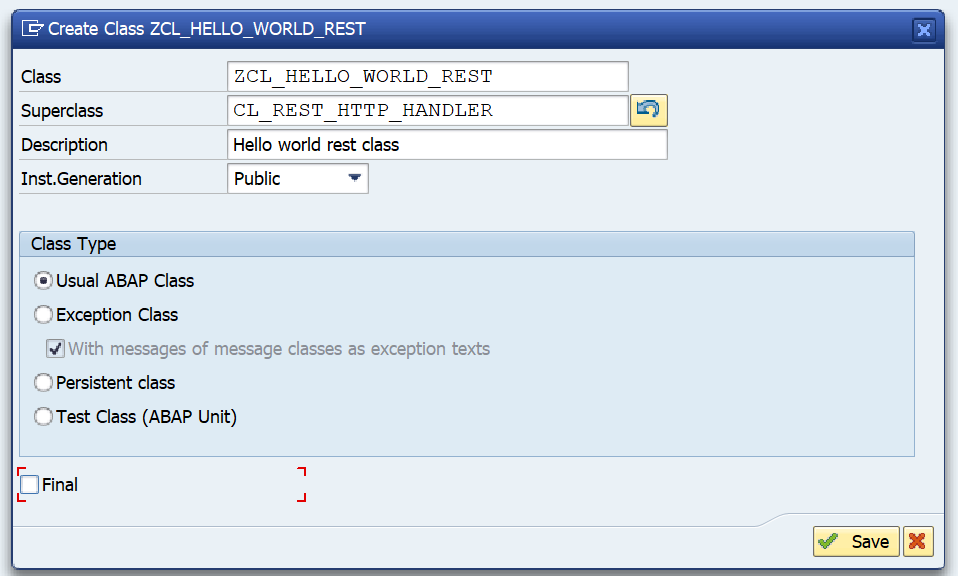
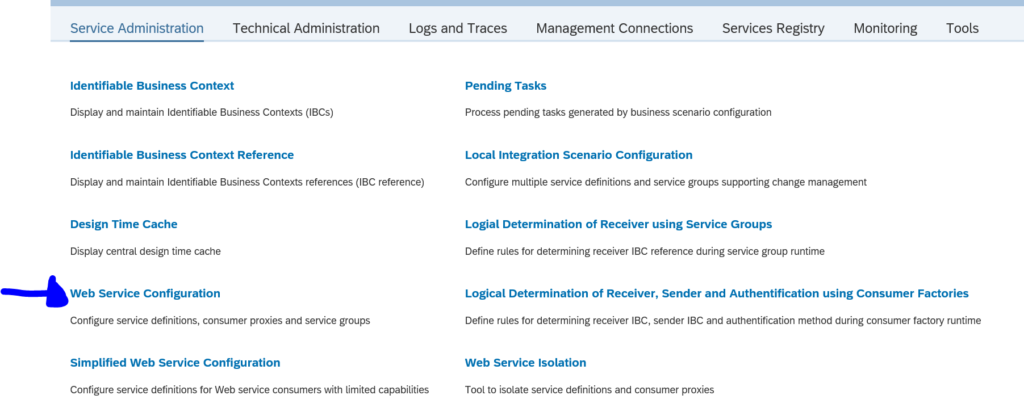
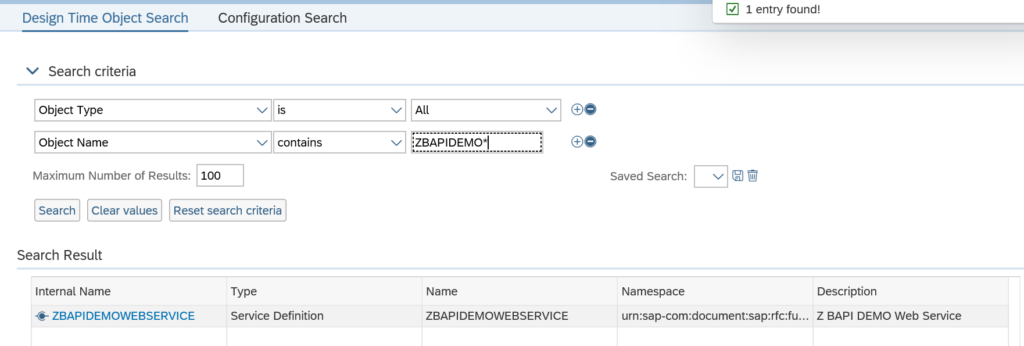
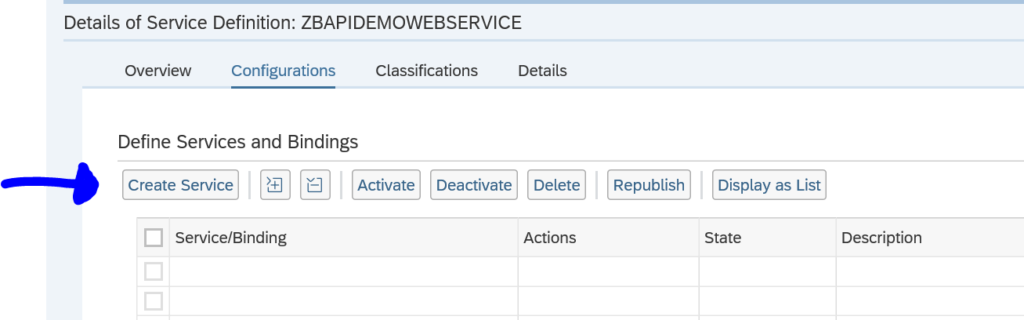
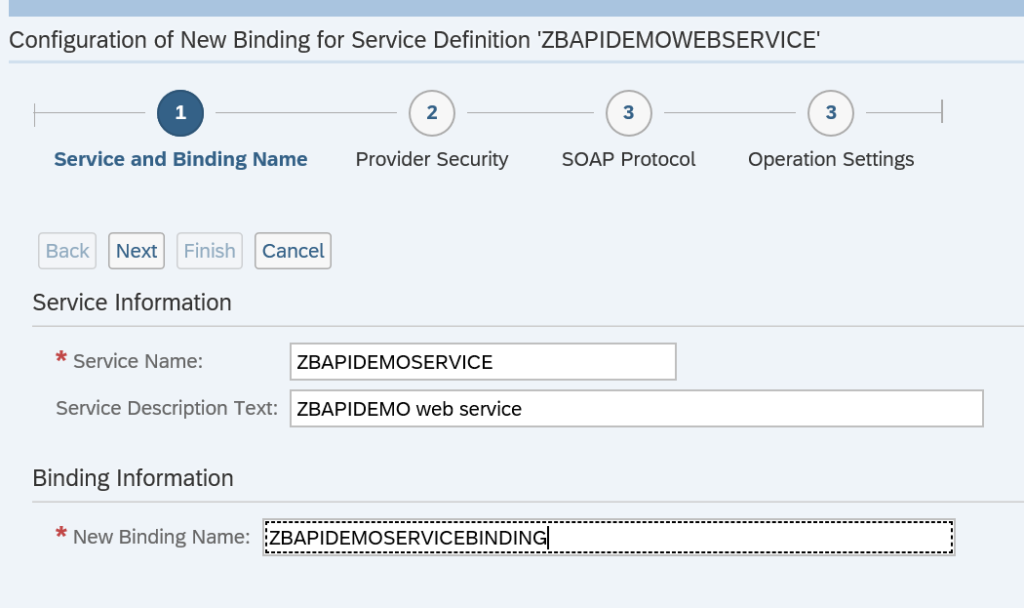
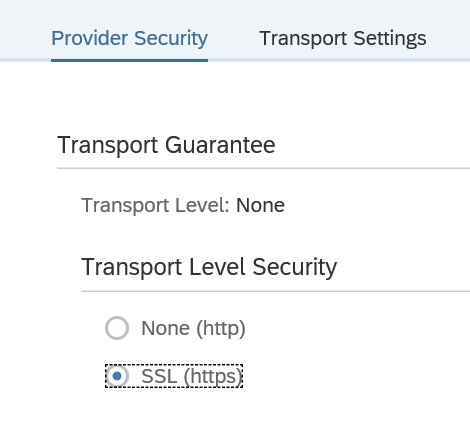
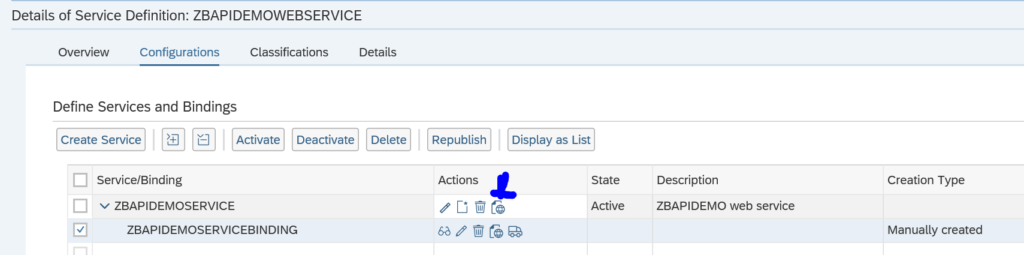
First in SE80 we create a OAUTH client profile named ZOAUTH_CLIENT_PROFILE_CPI:
Then the rest of the ABAP coding is according to the SAP help file, including the error handling on issues you might face.
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Report Z_CALL_API_USING_OAUTH
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
*&
*&--------------------------------------------------------------------*
REPORT z_call_api_using_oauth.
PARAMETERS:
zp_url TYPE string LOWER CASE
DEFAULT 'https://apimanagement.eu10.hana.ondemand.com/v1/api/hc/xxx/call_name',
zp_sslid TYPE strustssl-applic DEFAULT 'ANONYM',
zp_profl TYPE oa2c_profiles-profile DEFAULT 'ZOAUTH_CLIENT_PROFILE_CPI',
zp_confg TYPE oa2c_client-configuration DEFAULT 'ZOAUTH_CLIENT_PROFILE_CPI'.
CONSTANTS:
BEGIN OF zgcs_create_return,
argument_not_found TYPE sy-subrc VALUE 1,
plugin_not_active TYPE sy-subrc VALUE 2,
internal_error TYPE sy-subrc VALUE 3,
others TYPE sy-subrc VALUE 4,
END OF zgcs_create_return.
START-OF-SELECTION.
" oData: restrict to two entries returned, via url
DATA(zgv_api_url) = |{ zp_url }?$top=2|.
cl_http_client=>create_by_url( EXPORTING url = zgv_api_url
ssl_id = zp_sslid
IMPORTING client = DATA(zlo_http_client)
EXCEPTIONS argument_not_found = zgcs_create_return-argument_not_found
plugin_not_active = zgcs_create_return-plugin_not_active
internal_error = zgcs_create_return-internal_error
OTHERS = zgcs_create_return-others ).
CASE sy-subrc.
WHEN zgcs_create_return-argument_not_found.
MESSAGE 'Argument not found when trying to create http client instance' TYPE 'E'.
WHEN zgcs_create_return-plugin_not_active.
MESSAGE 'Plugin not active for creation of http client instance' TYPE 'E'.
WHEN zgcs_create_return-internal_error.
MESSAGE 'Internal error when trying to create http client instance' TYPE 'E'.
WHEN zgcs_create_return-others.
MESSAGE 'Generic error when trying to create http client instance' TYPE 'E'.
ENDCASE.
zlo_http_client->propertytype_logon_popup = zlo_http_client->co_disabled.
TRY.
DATA(zgo_oauth_client) = cl_oauth2_client=>create( i_profile = zp_profl
i_configuration = zp_confg ).
CATCH cx_oa2c_config_not_found.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Configuration not found' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_config_profile_assign.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Config - Unassigned Profile' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_kernel_too_old.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client - Kernel too old' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_missing_authorization.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client missing authorization' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_config_profile_multi.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Config - Profile assigned multiple times' TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.
" Set oAuth token to the http client
TRY.
zgo_oauth_client->set_token( io_http_client = zlo_http_client
i_param_kind = if_oauth2_client=>c_param_kind_header_field ).
CATCH cx_oa2c_at_not_available
cx_oa2c_at_expired.
" When setting the token fails, first try and get a new token
TRY.
zgo_oauth_client->execute_cc_flow( ).
CATCH cx_oa2c_badi_implementation.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client BAdI Impl. Error' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_not_supported.
MESSAGE 'Not supported by Service Provider.' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_not_allowed.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Not Allowed' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_prot_http_failure.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - HTTP Failure' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_prot_other_error.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Other Error' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_prot_unexpected_code.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Unexpected Code' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_prot_http_forbidden.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - HTTP 403 - Forbidden' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_prot_http_not_found.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - HTTP 404 - Not Found' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_server_error.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Server Error' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_temporarily_unavail.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Temporarily Unavailable' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_unsupported_grant_type.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Unsupported Grant Type' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_unauthorized_client.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Unauthorized Client' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_invalid_scope.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Invalid Scope' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_invalid_grant.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Invalid Grant' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_invalid_client.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Invalid Client' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_invalid_request.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime Protocol - Invalid Request' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_invalid_parameters.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Invalid Parameters' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_secstore_adm.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - SecStore Administration' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_secstore.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Secstore' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_protocol_exception.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Protocol Exception' TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.
" Set oAuth token to the http client
TRY.
zgo_oauth_client->set_token( io_http_client = zlo_http_client
i_param_kind = if_oauth2_client=>c_param_kind_header_field ).
CATCH cx_oa2c_at_not_available.
MESSAGE 'oAuth 2.0: Acces token not available' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_at_expired.
MESSAGE 'Access Token has expired.' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_at_profile_not_covered.
MESSAGE 'Access token has expired.' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_not_supported.
MESSAGE 'Not supported by Service Provider.' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_badi_implementation.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client BAdI Impl. Error' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_secstore.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Secstore' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_invalid_parameters.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Invalid Parameters' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_icf_error.
MESSAGE 'Unknown error received from ICF.' TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.
CATCH cx_oa2c_at_profile_not_covered.
MESSAGE 'Access token has expired.' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_not_supported.
MESSAGE 'Not supported by Service Provider.' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_badi_implementation.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client BAdI Impl. Error' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_secstore.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Secstore' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_invalid_parameters.
MESSAGE 'OAuth 2.0 Client Runtime - Invalid Parameters' TYPE 'E'.
CATCH cx_oa2c_icf_error.
MESSAGE 'Unknown error received from ICF.' TYPE 'E'.
ENDTRY.
" From here on handle the http client for the API interaction
zlo_http_client->request->set_version( if_http_request=>co_protocol_version_1_0 ).
DATA(zlo_rest_client) = NEW cl_rest_http_client( io_http_client = zlo_http_client ).
" Get data from API
TRY.
zlo_rest_client->if_rest_client~get( ).
" Collect response received from the REST API
DATA(zli_response) = zlo_rest_client->if_rest_client~get_response_entity( ).
DATA(zgv_http_status_code) = zli_response->get_header_field( `~status_code` ).
DATA(zgv_status_reason) = zli_response->get_header_field( `~status_reason` ).
DATA(zgv_response_data) = zli_response->get_string_data( ).
" Record the response of the interface
IF zgv_http_status_code BETWEEN 200 AND 299.
" Success
MESSAGE 'Call was succesful' TYPE 'S'.
ELSE.
MESSAGE 'Call failed' TYPE 'E'.
ENDIF.
WRITE / 'Response'.
WRITE / zgv_response_data.
" Issues with REST client must not lead to a short-dump
CATCH cx_rest_client_exception INTO DATA(zlx_rest_client).
IF zlx_rest_client->if_t100_message~t100key IS NOT INITIAL.
DATA zlv_message TYPE string.
MESSAGE ID zlx_rest_client->if_t100_message~t100key-msgid
TYPE 'E'
NUMBER zlx_rest_client->if_t100_message~t100key-msgno
WITH zlx_rest_client->if_t100_message~t100key-attr1
zlx_rest_client->if_t100_message~t100key-attr2
zlx_rest_client->if_t100_message~t100key-attr3
zlx_rest_client->if_t100_message~t100key-attr4.
ELSE.
MESSAGE 'Rest client Exception' TYPE 'E'.
ENDIF.
ENDTRY.
zlo_http_client->close( ).