In the previous blog we have created a test RFC module. We now will expose this test RFC module as web service. This blog assumes the basic SOAP web service runtime has been done according to the manual in this blog.
If you are looking for information on how to consume a web service in the ABAP stack: read this blog.
Questions that will be answered are:
- How can I generate a web service design time based on an RFC module?
- How do I activate the web service runtime via SOAMANAGER?
- How do I test my web service?
Creating the web service based on RFC module
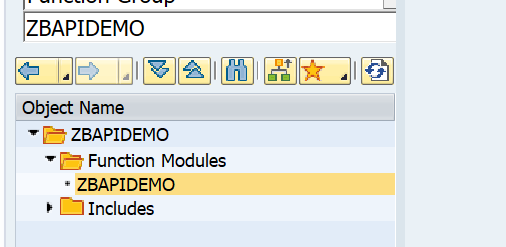
Goto transaction SE80 and search for the test BAPI:
Now right click on the name ZBAPIDEMO function module and select the option Create / Enterprise Service:
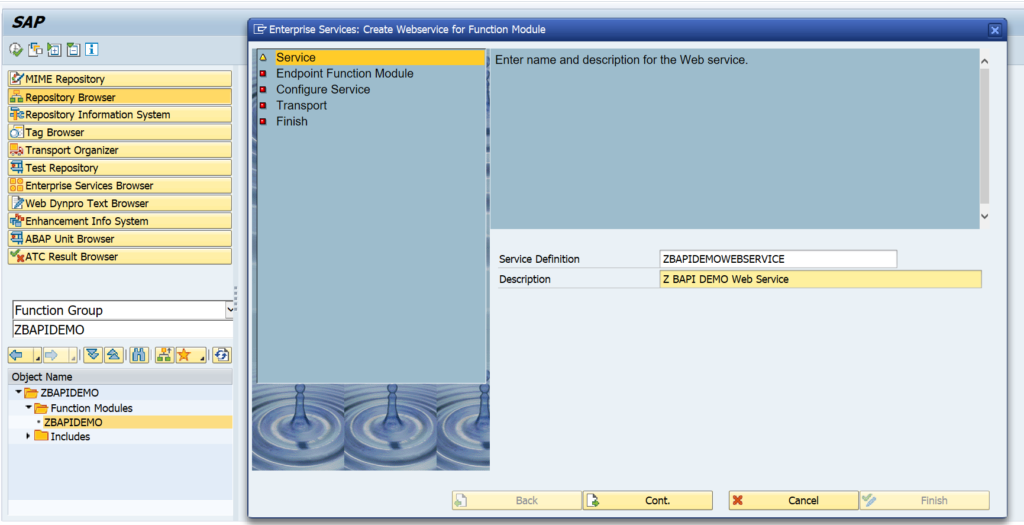
Fill out the name for the service definition and the description. Press Cont. to continue to the next screen:
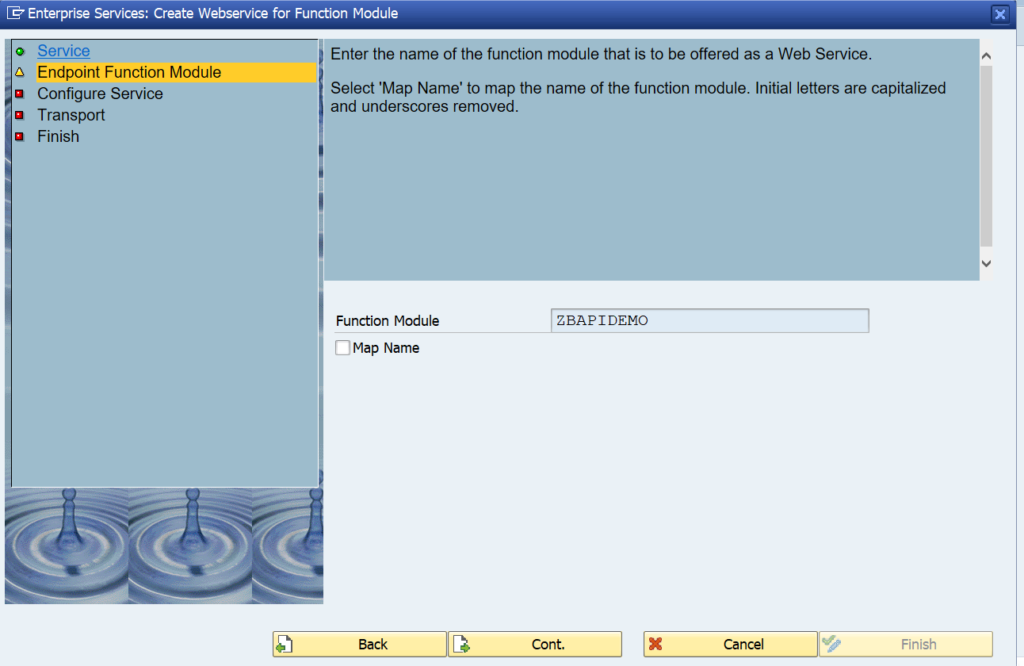
Press Cont to go to the next step:
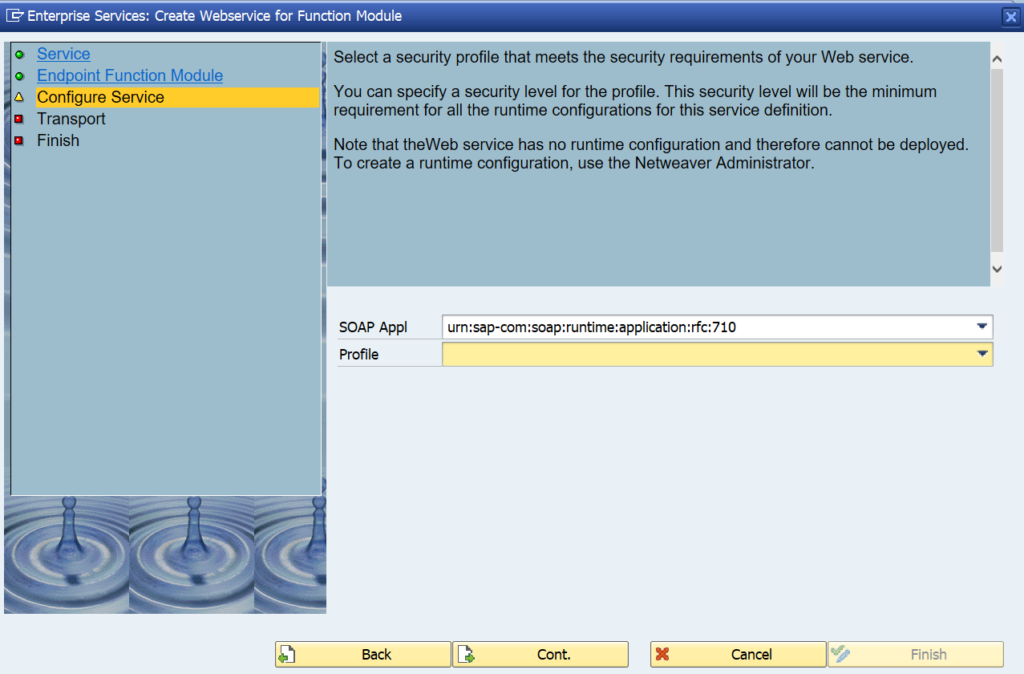
Press Cont. to go to the next screen:
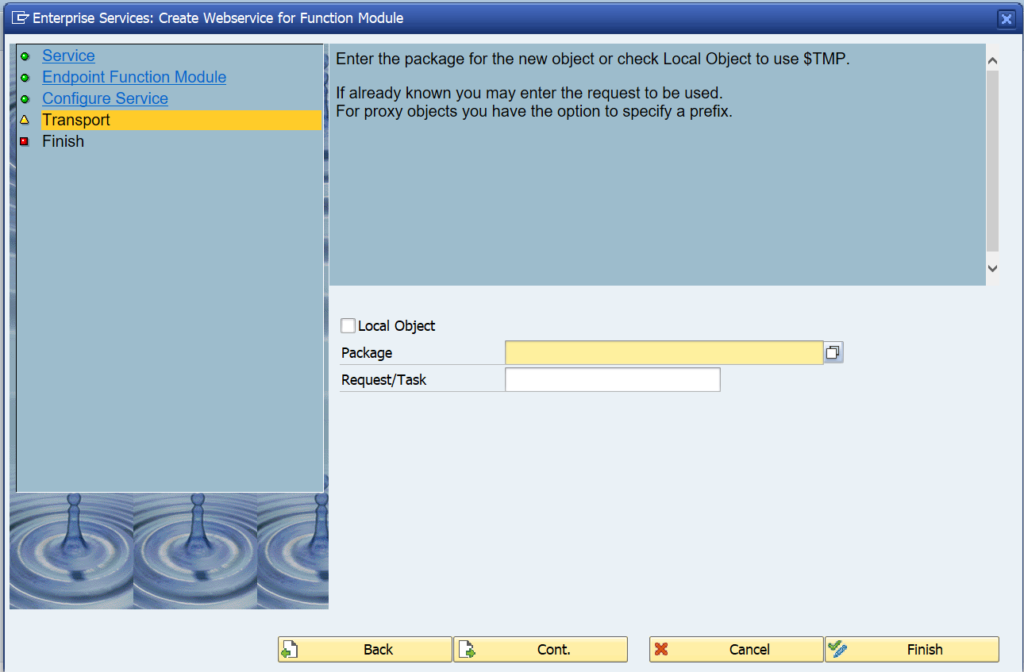
Fill out your package and transport request.
Important here: on a sandbox you might want to use a local object ($TMP). In a development system, NEVER use the local option. A lot of data structures and coding will be generated. If you later try to move the objects from $TMP to a real package, you will be faced with a lot of issues. See note 886682 - Proxy inconsistencies on the use of repair programs SXIVERI_PROXY_HASHID_CHECK and SXIVERI_PROXY_HASHID_CHECK_70. After the cumbersome and painfull repair you will not make the mistake again...
Press Cont. to goto the last screen:
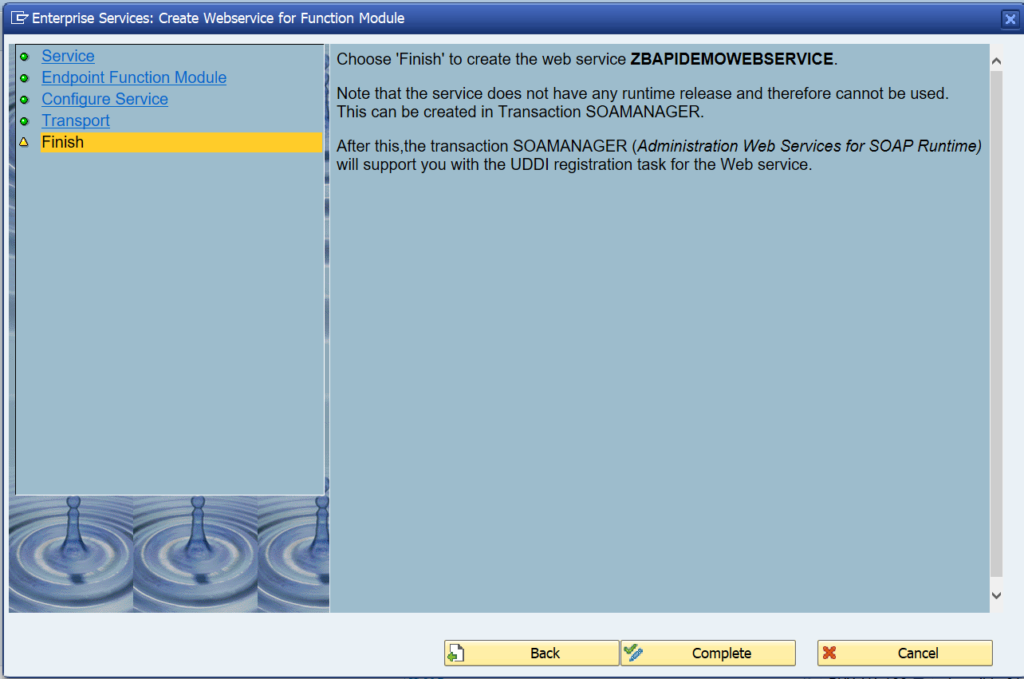
On the screen you can already see the next action after completion: SOAMANAGER. But first press Complete to start the generation of the objects.
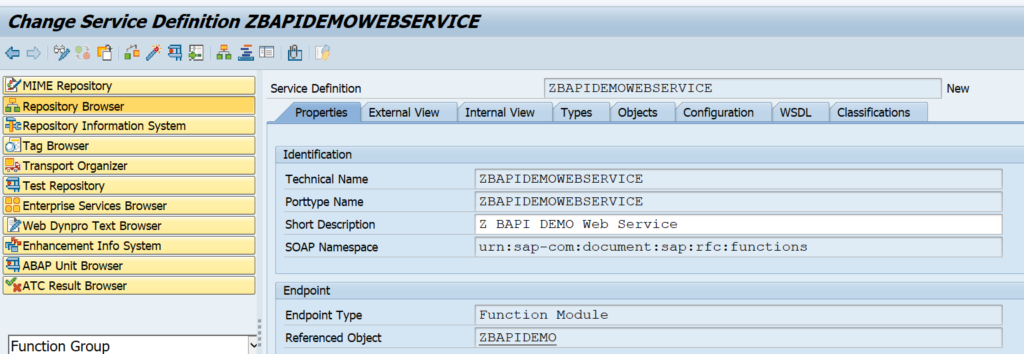
After the generation, do not forget to Activate the objects!
Activation success message:
Setting up the runtime with SOAMANAGER
To setup the runtime, start transaction SOAMANAGER. It is assumed that the basis team has performed the initial SOAP runtime setup. If not done, ask the basis team to follow the steps in this blog.
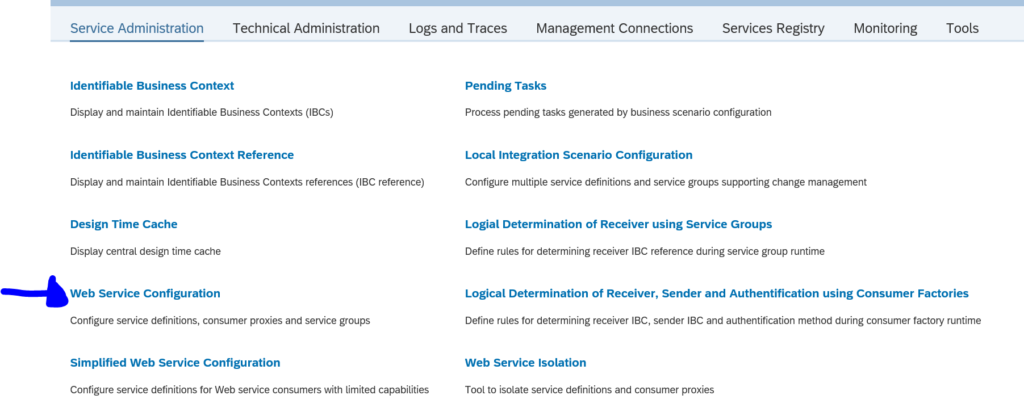
On the SOAMANAGER start screen choose the option Web Service Configuration:
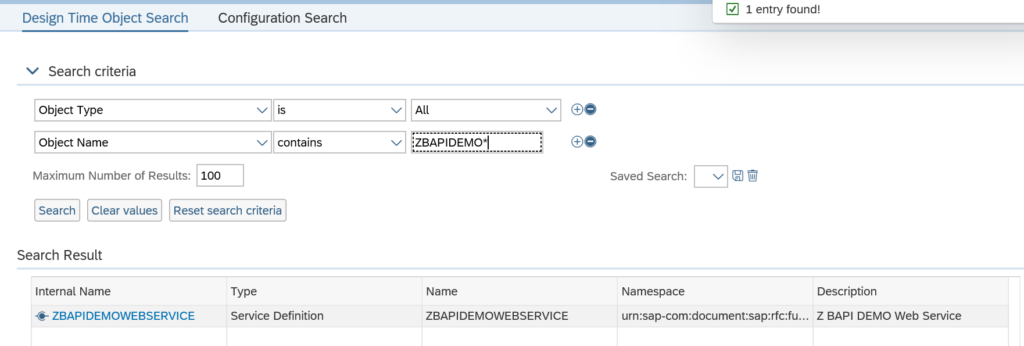
In the next screen search for the design time object we created and activated in the previous section (if you forgot the activate, you will not find it now…):
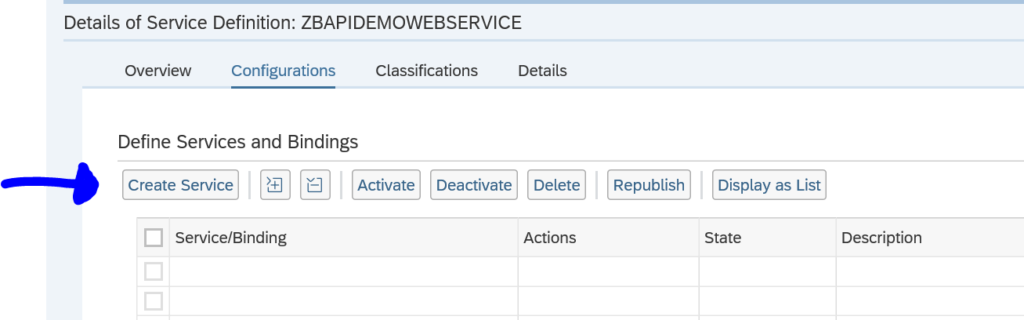
Select the service and on the next screen press the button Create Service:
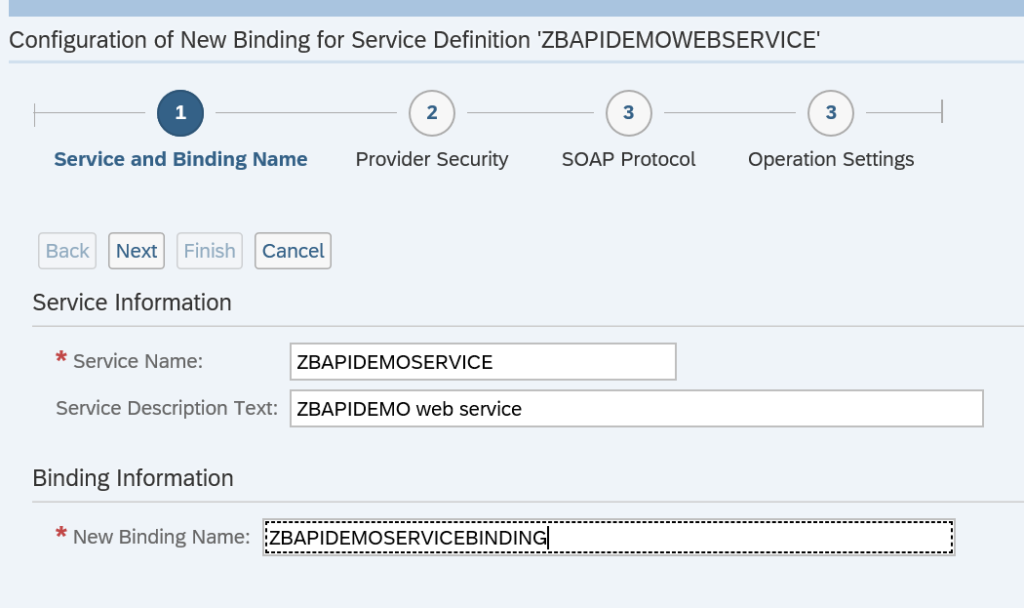
Fill out the definition details:
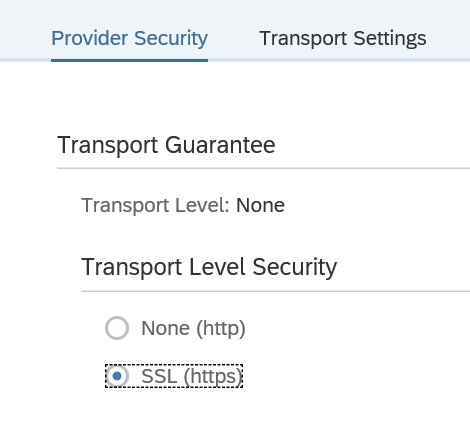
Press Next and define the security settings:
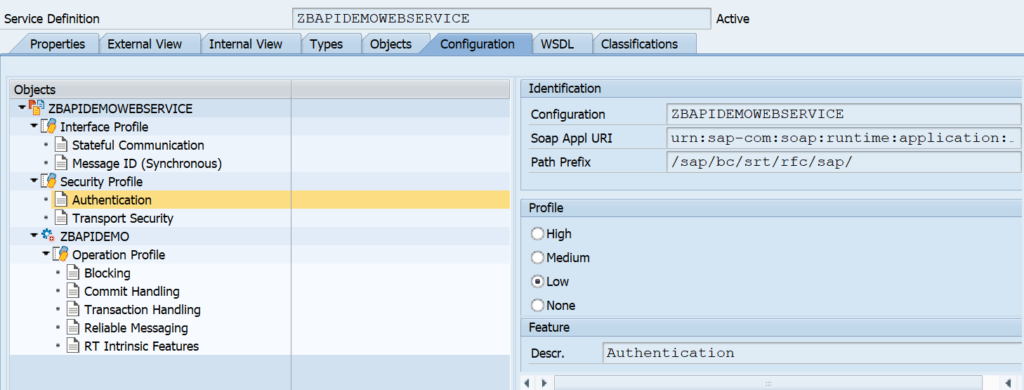
Remark: in the newer versions, the default security is set to high. If you need lower security, go back to SE80 definition in the tab configuration to change the security profile (save and regenerate!):
Press next and define the SOAP protocol settings:
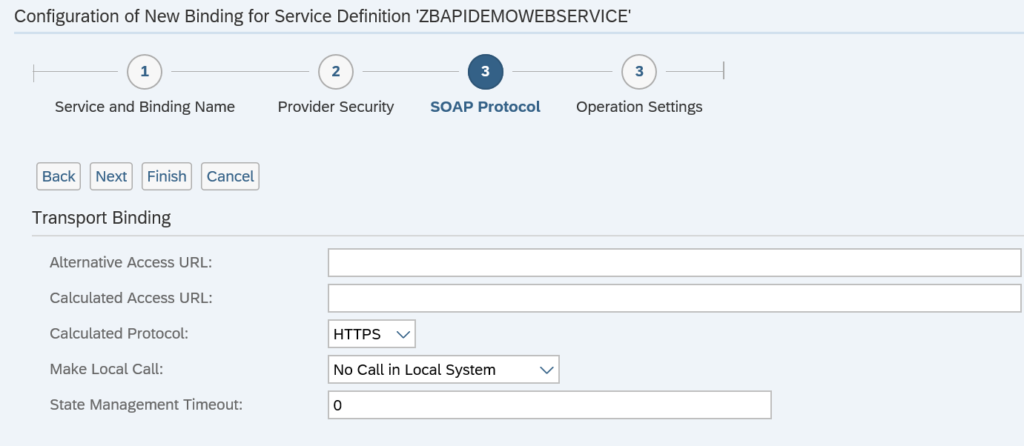
On the last screen of the wizard press finish:
Wait for the runtime generation to finish.
The screen returns to the generated runtime artifacts:
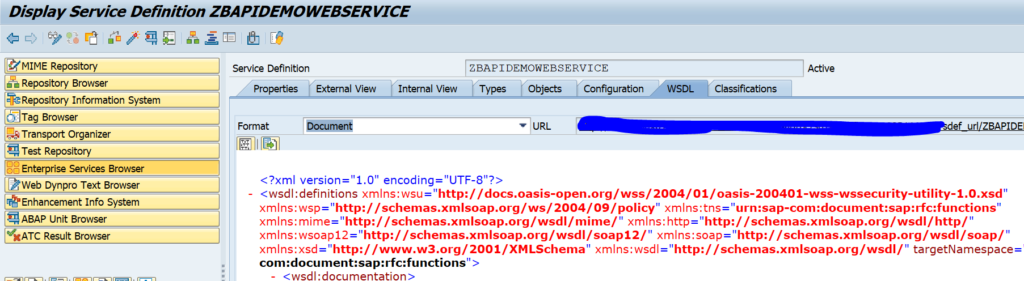
The most important artifact is WSDL file which you can open from here.
Testing the service
Go to transaction SE80 and select the Enterprise Services Browser (if not visible go to menu path Utilities/Settings and add the tool):
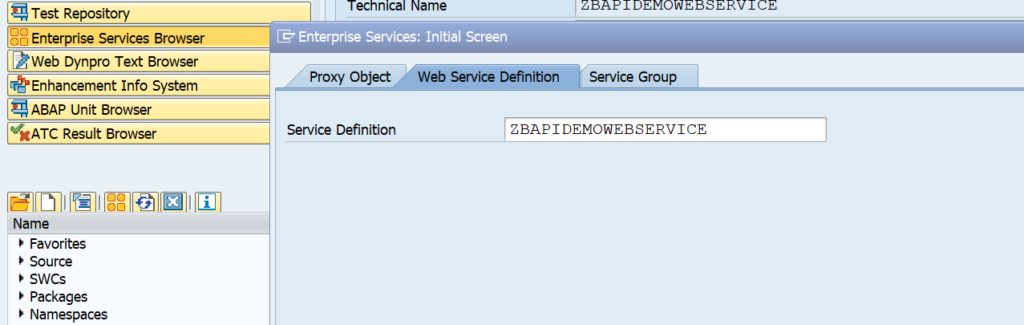
Now open your service by clicking the Open Object button and search for the service in the second tab:
Check that the WSDL file is properly showing:
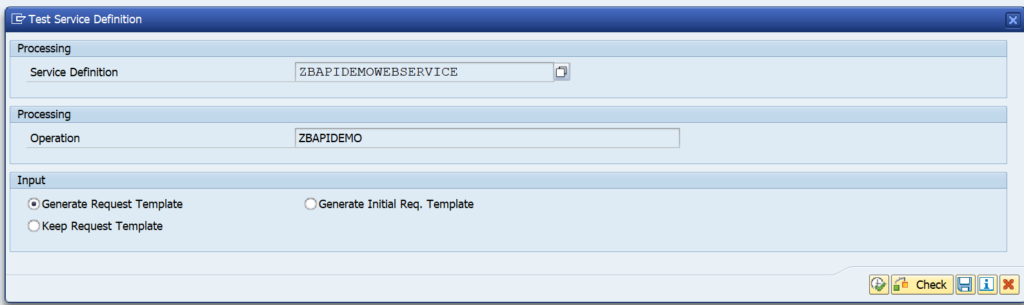
If ok, press the test button (F8) to start the test tool:
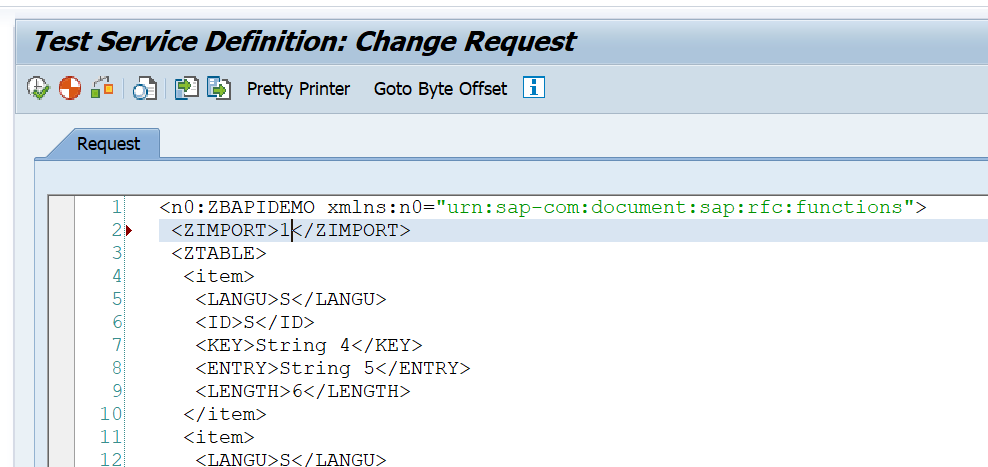
On the next screen first press the XML editor button to allow the content to be changed:
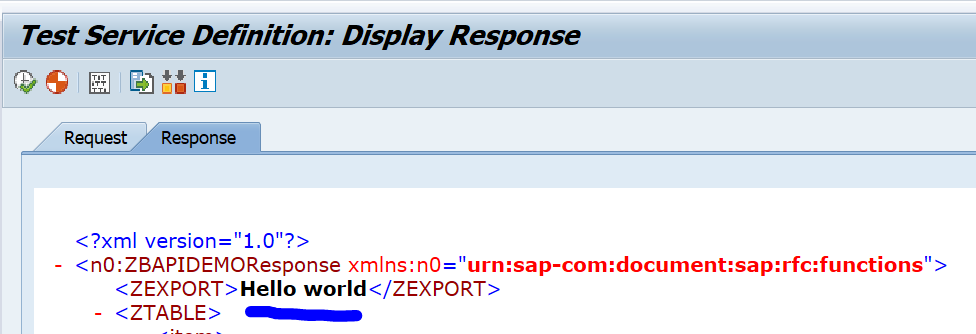
Now press execute to test. The result:
Web service security
The functionality security of the web service is the same as for the generic RFC handling (see blog on this).
The technical security of web services is mainly driven from the security settings in SOAMANAGER. There you can set the transport protocol security and you can indicate if you want simple user ID / password security or work with additional certificates for server to server authentication.
The user calling the SAP web service must have the authorization object S_SERVICE. In S_SERVICE you can define the specific web service it needs to be able to call.
Troubleshooting web services security issues
For troubleshooting web services note 2321968 – SOAP Web Service Security Troubleshooting refers to a very extensive SAP site for web service security issues troubleshooting.
Monitoring web services
For monitoring web services messages, read this dedicated blog.
To validate if the web services is correctly accessible, you need a small Z program as described in this blog.