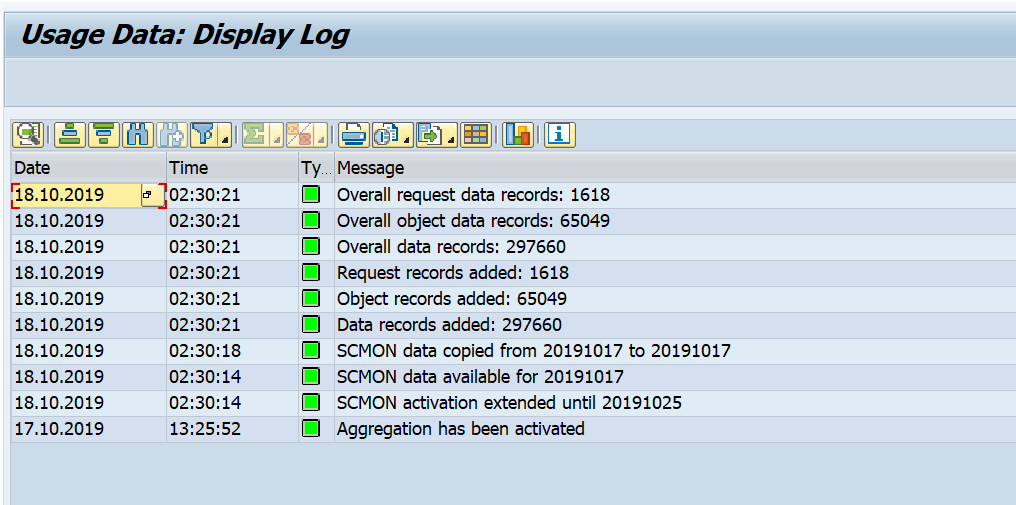
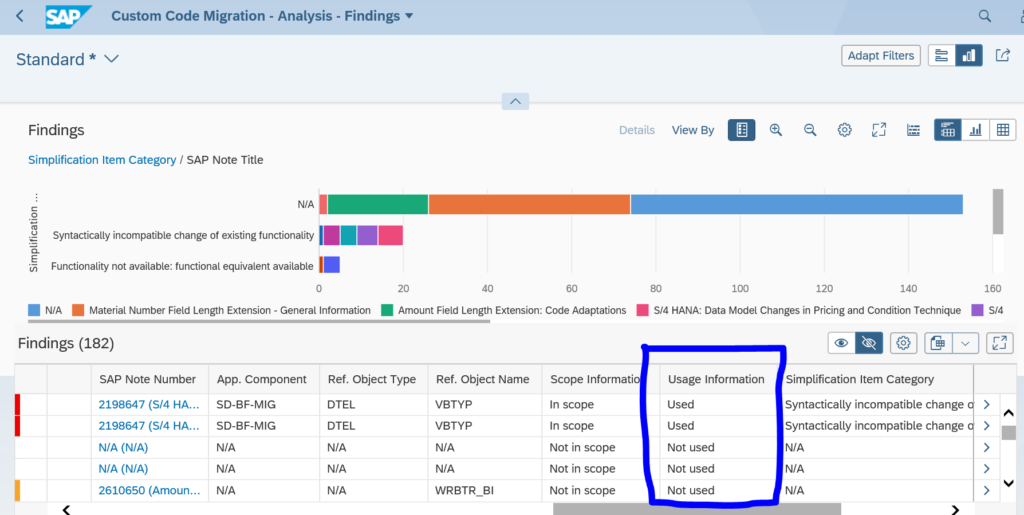
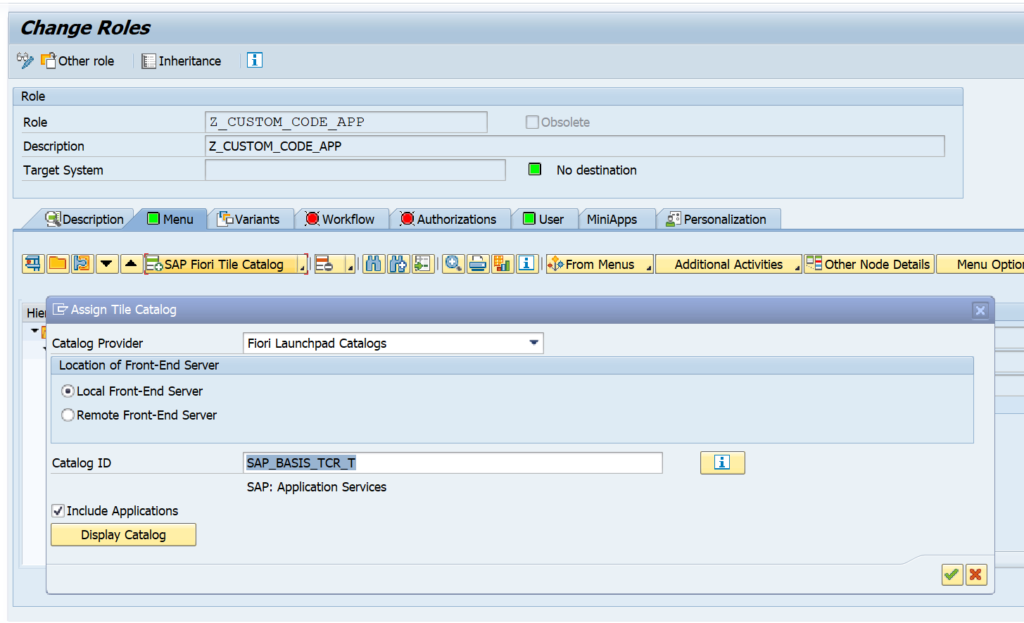
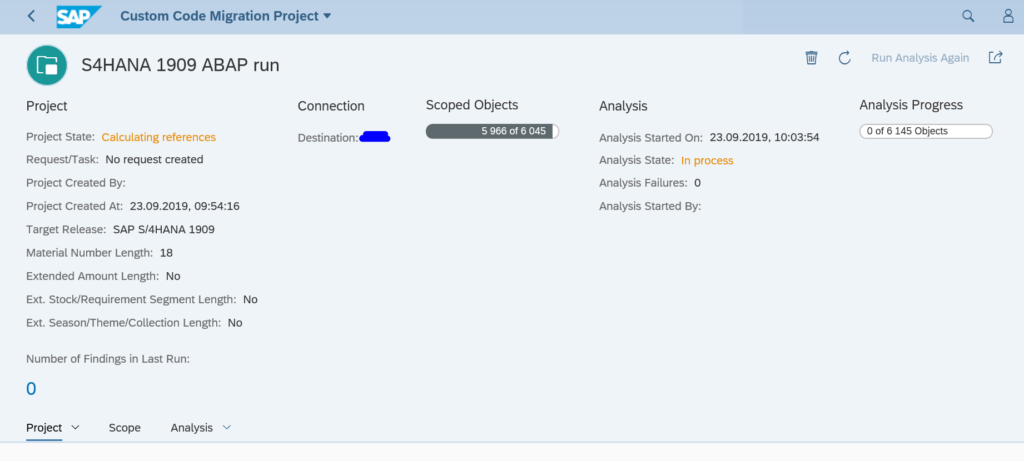
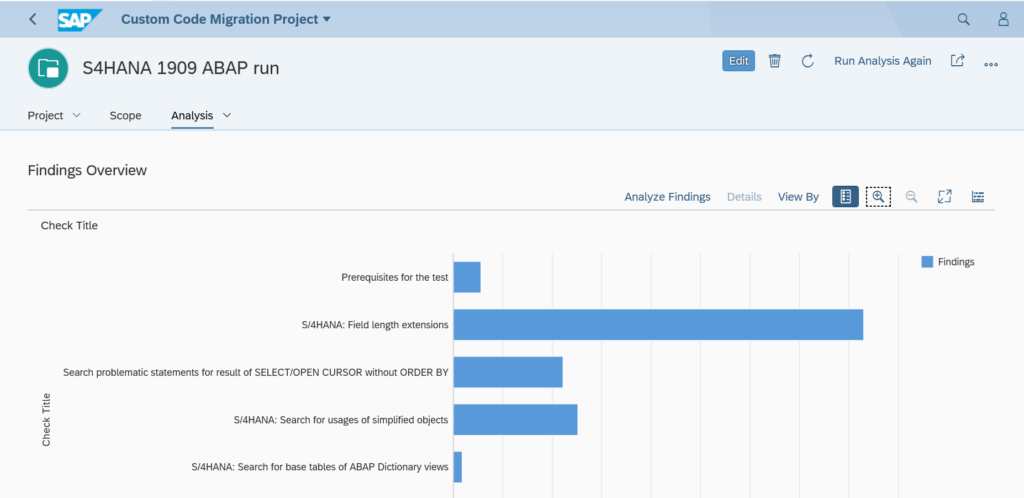
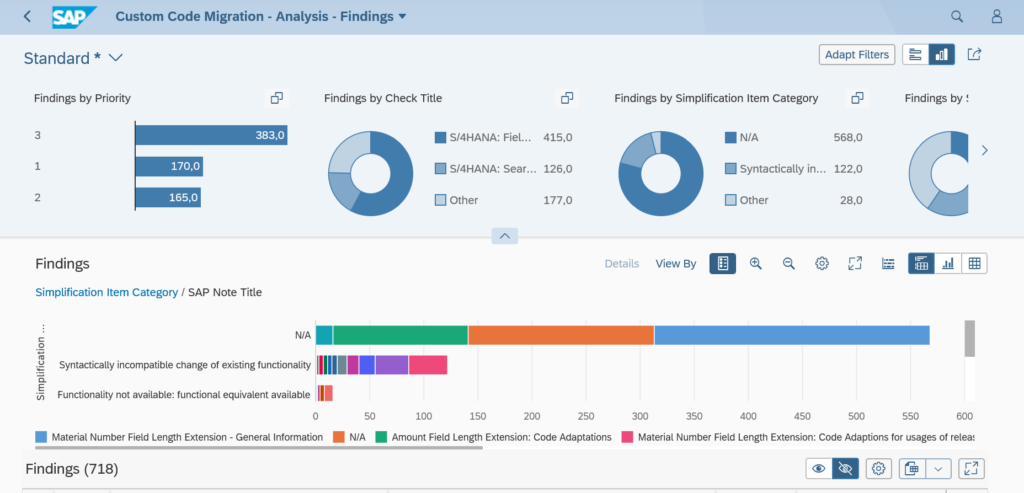
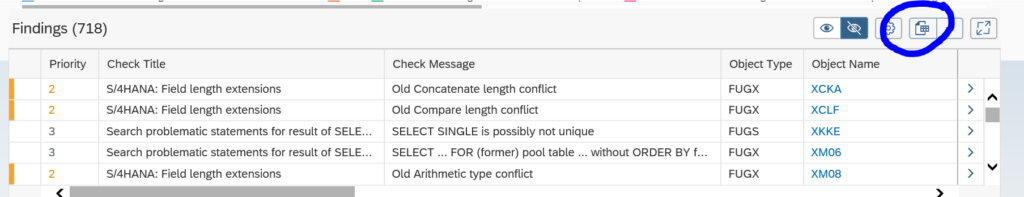
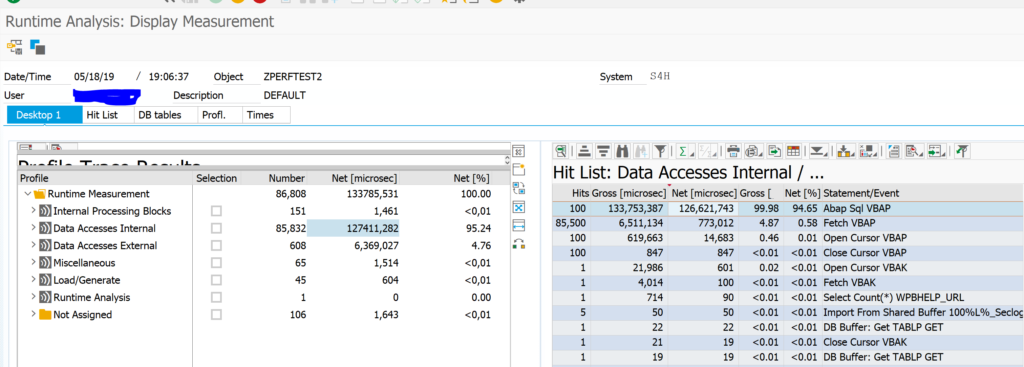
You have just upgraded to S4HANA in your sandbox or development system. SPAU and SPAU_ENH processing are done. Next step is the S4HANA custom code adjustments.
Questions that will be answered in this blog are:
- How to import the SCI variants for S4HANA custom code adjustments?
- How to import the latest simplification database into your system?
- How to run the S4HANA custom code adjustments in ATC tool?
- How to enable quick fixes in Eclipse?
Importing the SCI variants
Goto transaction SCI and select the option Utilities and then Import Check Variants. This action will import the required variants. Check that the variants are present now.
In case you don’t want to do the field length extensions checks, choose the variant with _NO_FLE at the end.
1909: 2925563 – Check variants for S/4HANA custom code checks without field length extensions.
2020: 2959341 – Check variant for SAP S/4HANA 2020 custom code checks.
2021: 3090106 – Check variant for SAP S/4HANA 2021 custom code checks.
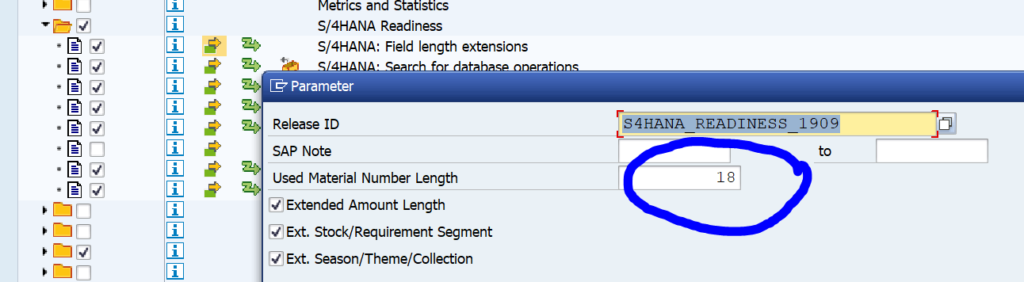
Otherwise: in the SCI variant, you can leave everything as delivered out-of-the-box with the exception of the material length option. If you keep the material field business wise to 18 (which most customers do), you need to change the variable from 40 to 18.
You can apply the bug fix notes listed in 2436688 – Recommended SAP Notes for using S/4HANA custom code checks in ATC or Custom Code Migration app.
Setting up the simplification database
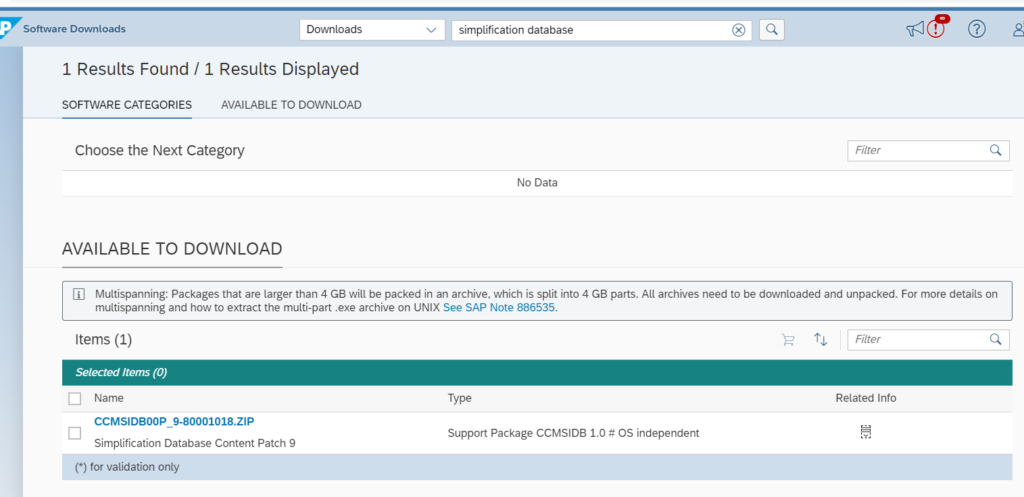
Follow the instructions of OSS note 2241080 – SAP S/4HANA: Content for checking customer specific code, to download the latest content for the simplification database.
Use transaction SYCM to upload the file. Select option Simplification Database and then Import from ZIP File.
Running the ATC tool
Now you can start to setup the ATC tool. For details see this blog.
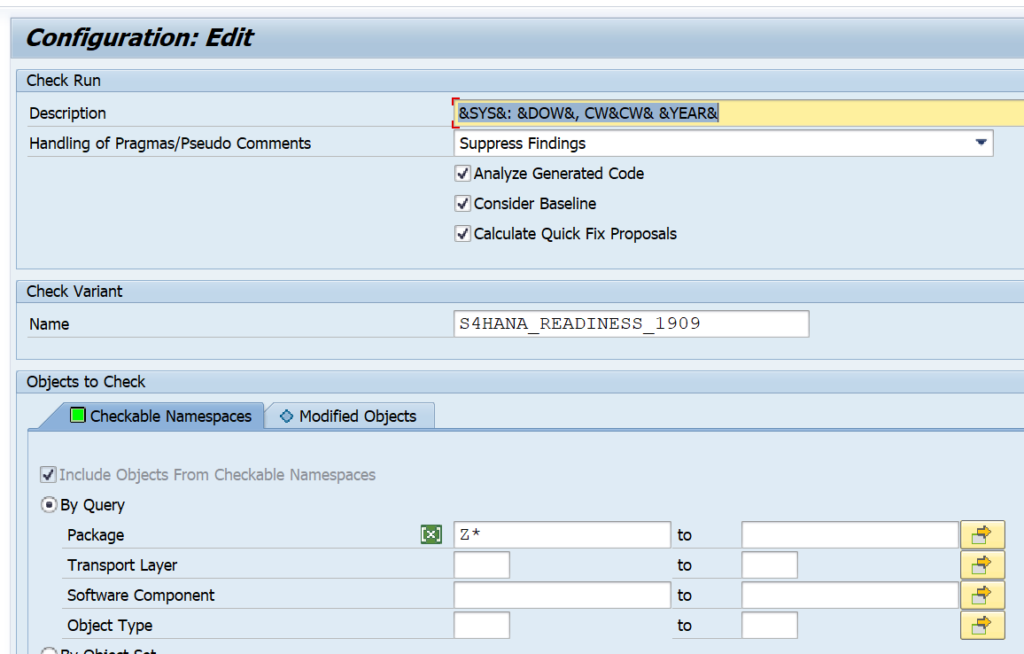
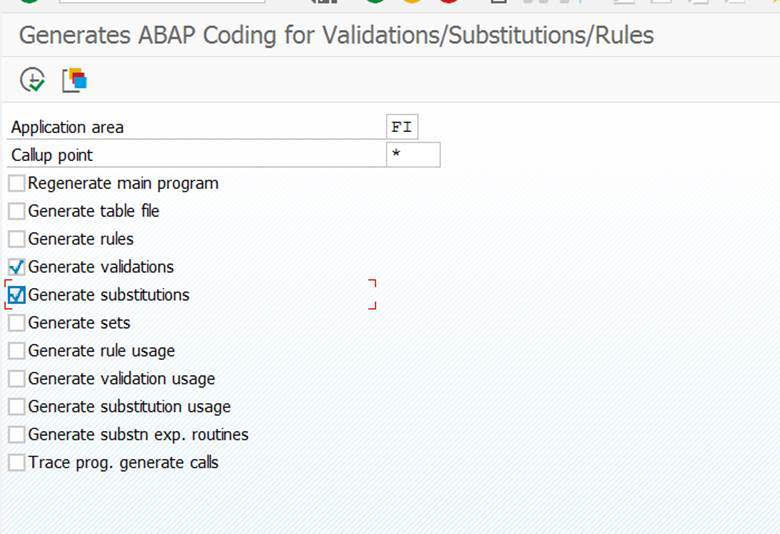
The ATC variant to run should like like this:
Important here:
- Select the desired S4HANA readiness check SCI variant
- Set the package to Z* to select your custom code
- Tick the box for Calculate quick fix proposals
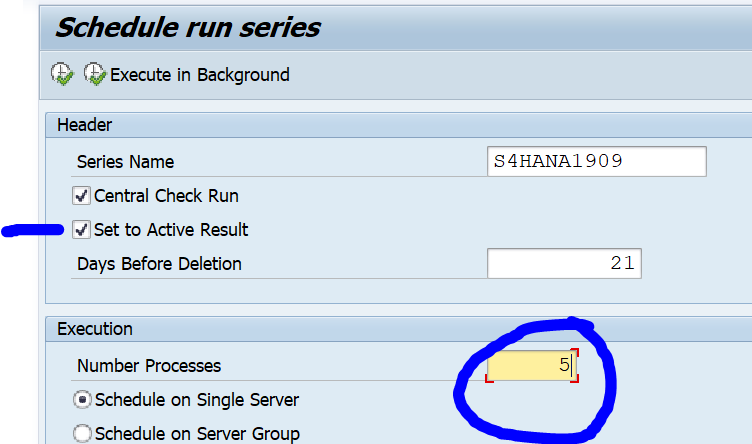
Now you can start the ATC run:
Set the results to Active to see all the results in Eclipse as well. Pending on your system size lower the default number of processes from 10 to for example 5.
If you run into ATC tool issues for the S4HANA custom code adjustments run: first increase memory parameter rsdb/obj/buffersize in RZ11 to at least 150 MB. Then run again.
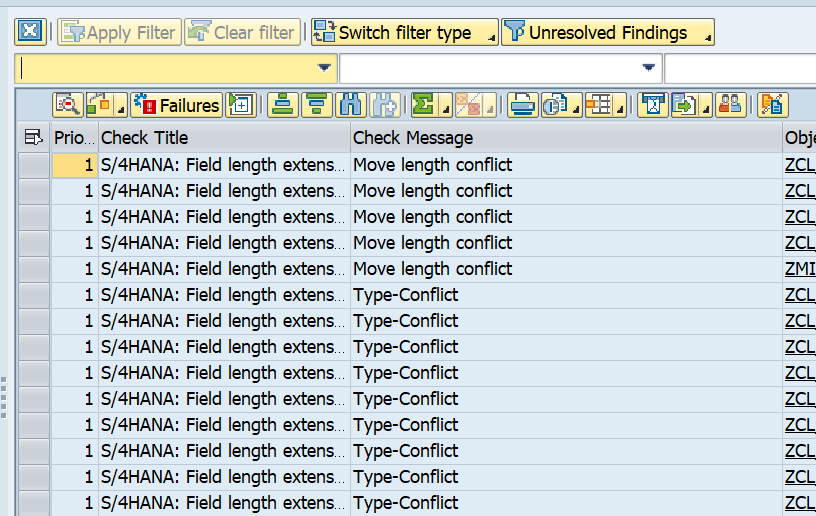
Processing the results
The ATC tool will now give a lot of results:
The results from the ATC tool can be distributed to more members by changing the Contact Person. To do this select one or more findings and right click on the Contact Person column, and select the option Change Contact Person.
The basic order of processing the results:
- Check simplification OSS note
- Fix code
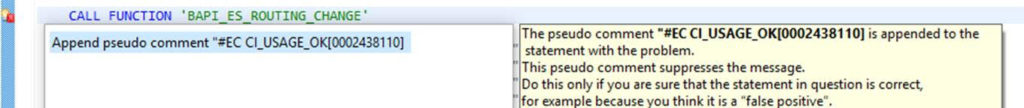
- Apply relevant pragma (directly or in Eclipse via quick fix)
- Apply exemption
For the exemptions: you can raise them, but different person needs to approve them.
When you are using Eclipse, you might run into issue with exemption request. See OSS note 2815887 - ATC: No Possibility to Request Exemptions in Eclipse for the fix.
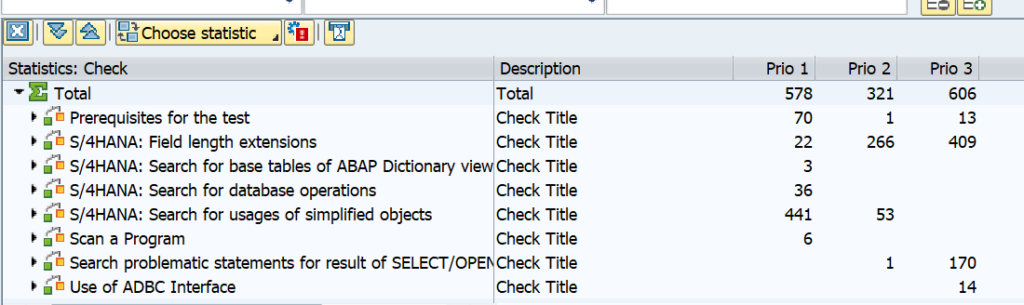
If you run the ATC tool weekly, you can use it to track the progress. In the ATC results screen there is a specific button Statistics View:
Default sorting is by type of issue to be solved:
This view can also be sorted on Contact Person. This will enable you to check the progress of each developer with his or her work list.
Using quick fixes with Eclipse
Using quick fixes with Eclipse is a fast way of going through the list. The Eclipse list is based on Contact Person and active results. So you only see in Eclipse the results for your user account.
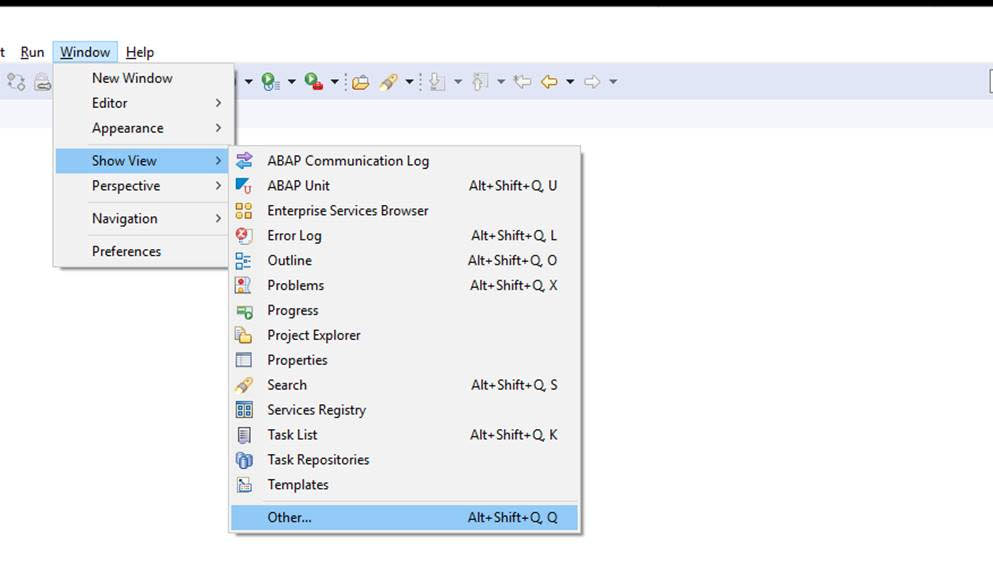
In Eclipse first select the appropriate views:
Now you can start processing. You will get online help and you can apply the quick fix proposed automatically in stead of keying it in by hand.
You might run into an initial bug with a dump, which is solved by applying OSS note 2647710 - Simple transformation: Inconsistent ST loads.
The quick fixes are updated with both bugs and new functions. Please check out the new versions of the following OSS notes:
Nice blog on the quick fixes: follow this link.
To enable ABAP backend for Eclipse: follow this link.
Using the S4HANA custom code migration app
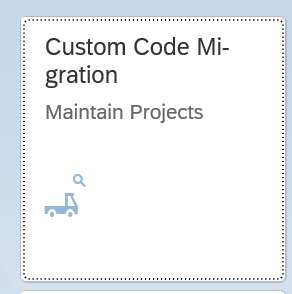
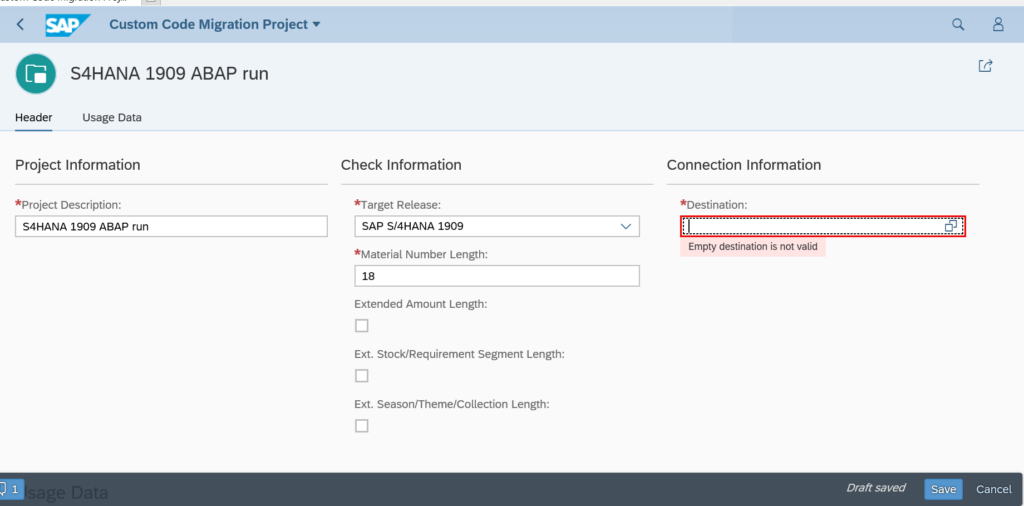
You can also use the S4HANA custom code migration app. After completing the setup above and activating the S4HANA embedded FIORI (see this blog), you simply follow the steps in this blog for the setup.
ABAP clones
In the past copies of standard SAP might have been made. These are so called clones. You can use the clone finder tool to detect the clones. Consider to delete the clones completely. Most of the times the clone is no longer required. This will save you work on the code migration. How to run the clone finder tool can be read in this dedicated blog.
Use of unreleased standard SAP objects
Developers might have been using standard SAP objects, which formally have an unreleased status, and might no longer be supported by S4HANA. Read this blog to find out how you can scan your custom code for use of unreleased standard SAP objects.
Further background information
More information can be found: